Page 430 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 430
396 Chapter 3
flow characteristics. Hemorrhage can be differentiated capillary breakdown. In horses’ feet, significant con
63
117
into acute and chronic stages on MR images. In the trast enhancement has been observed in tendinopathy
VetBooks.ir on T1‐weighted images and hyperintense on T2‐ the distal sesamoidean impar ligament and the collateral
lesions of the deep digital flexor, desmopathy lesions of
acute stage, hemorrhage is like other fluids, hypointense
weighted images. After approximately one week,
sesamoidean ligaments, synovitis (also septic) of the DIP
methemoglobin release leads to increased T1 signal joint, and palmar erosions of the flexor cortex of the
intensity. In the chronic stage, hemosiderin will cause navicular bone (Figure 3.219). 85,154 In the brain, gado
zero signal areas to appear due to susceptibility artifacts linium causes significant enhancement of inflammatory
especially on GRE images. Susceptibility artifacts may and neoplastic lesions because of their increased vascu
20
persist indefinitely at the site of previous hemorrhage larity and ability to break down the blood–brain
due to injection, surgical intervention like arthroscopy, barrier. 64,109
181
or injury. The center of old hemorrhage may remain Direct MRI arthrography with a saline–gadopentetate
hyperintense on T1‐weighted and T2‐weighted images dimeglumine mixture (1.0 mL gadopentetate dimeglu
due to persistence of methemoglobin. mine/250 mL saline; 2–4 mmol/L) has been used in the
assessment of complex intra‐articular soft tissue structures
CONTRAST MRI TECHNIQUES in human patients. With respect to cartilage imaging,
MRI arthrography has reportedly resulted in at least
MRI contrast medium was developed to enable 10% improvement in chondral lesion detection relative
differentiation between two tissues with similar MR to conventional MRI studies. 97,181 Higher concentrations
characteristics by differentially increasing their signal cause signal blackout and nondiagnostic images due to
intensity in the presence of injury. Gadolinium is a para strong magnetic susceptibility effects. Better cartilage
magnetic contrast agent that enhances T1 relaxation contrast may be achieved following direct MRI arthrog
and thus shortens T1 relaxation times, resulting in raphy with saline than with gadolinium, 35,100,102,159 as
increased signal in tissues containing this element on T1 saline (hypointense) results in better image contrast
images. between cartilage (medium high to high signal) and syn
Post‐contrast fat‐saturated T1‐weighted sequences ovial fluid than gadolinium (hyperintense) on T1
are obtained following intravenous administration of images. Distension of the navicular bursa or DIP joint
159
gadolinium diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid with 0.9% saline revealed adhesion formation, DDFT
(0.02 mmol/kg IV) or gadopentetate dimeglumine injury, and fibrocartilaginous damage to the navicular
64
85
(0.1 mL/kg IV). Local intravenous delivery of gado bone. 16,100,102
pentetate by regional limb perfusion with a tourniquet Indirect MRI arthrography is performed following
in the mid‐metacarpal region may provide similar results intravenous injection of paramagnetic MRI contrast
with lower dosages of contrast agent (5 mL gado media as indicated above. Similar sensitivities and
pentetate diluted with 5 mL of physiological saline per specificities have been reported for indirect MRI arthrog
distal limb). Gadopentetate dimeglumine leaks into the raphy when compared with direct MRI arthrography in
1
extracellular compartment to become detectable on MR the diagnosis of intra‐articular soft tissue injuries like
images following tissue injury with inflammation and tears of the rotator cuff, glenoid labrum, and menisci. 201
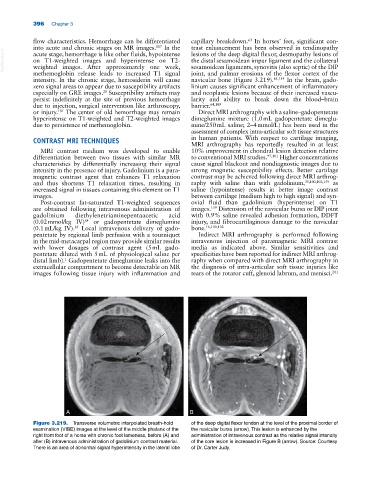
A B
Figure 3.219. Transverse volumetric interpolated breath‐hold of the deep digital flexor tendon at the level of the proximal border of
examination (VIBE) images at the level of the middle phalanx of the the navicular bursa (arrow). This lesion is enhanced by the
right front foot of a horse with chronic foot lameness, before (A) and administration of intravenous contrast as the relative signal intensity
after (B) intravenous administration of gadolinium contrast material. of the core lesion is increased in Figure B (arrow). Source: Courtesy
There is an area of abnormal signal hyperintensity in the lateral lobe of Dr. Carter Judy.