Page 547 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 547
560 31 Body Wall
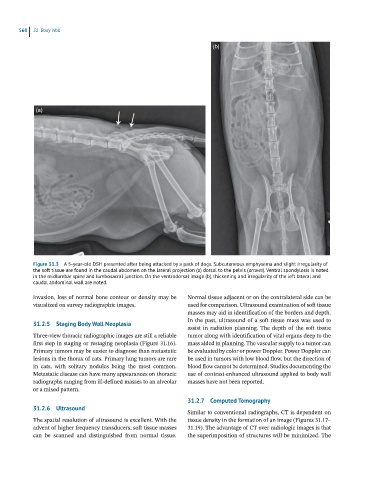
(b)
(a)
Figure 31.3 A 5-year-old DSH presented after being attacked by a pack of dogs. Subcutaneous emphysema and slight irregularity of
the soft tissue are found in the caudal abdomen on the lateral projection (a) dorsal to the pelvis (arrows). Ventral spondylosis is noted
in the midlumbar spine and lumbosacral junction. On the ventrodorsal image (b), thickening and irregularity of the left lateral and
caudal abdominal wall are noted.
invasion, loss of normal bone contour or density may be Normal tissue adjacent or on the contralateral side can be
visualized on survey radiographic images. used for comparison. Ultrasound examination of soft tissue
masses may aid in identification of the borders and depth.
In the past, ultrasound of a soft tissue mass was used to
31.2.5 Staging Body Wall Neoplasia
assist in radiation planning. The depth of the soft tissue
Three-view thoracic radiographic images are still a reliable tumor along with identification of vital organs deep to the
first step in staging or restaging neoplasia (Figure 31.16). mass aided in planning. The vascular supply to a tumor can
Primary tumors may be easier to diagnose than metastatic be evaluated by color or power Doppler. Power Doppler can
lesions in the thorax of cats. Primary lung tumors are rare be used in tumors with low blood flow, but the direction of
in cats, with solitary nodules being the most common. blood flow cannot be determined. Studies documenting the
Metastatic disease can have many appearances on thoracic use of contrast-enhanced ultrasound applied to body wall
radiographs ranging from ill-defined masses to an alveolar masses have not been reported.
or a mixed pattern.
31.2.7 Computed Tomography
31.2.6 Ultrasound
Similar to conventional radiographs, CT is dependent on
The spatial resolution of ultrasound is excellent. With the tissue density in the formation of an image (Figures 31.17–
advent of higher frequency transducers, soft tissue masses 31.19). The advantage of CT over radiologic images is that
can be scanned and distinguished from normal tissue. the superimposition of structures will be minimized. The