Page 564 - Feline diagnostic imaging
P. 564
sAsesiesi 577
(b)
(a)
(c) (d)
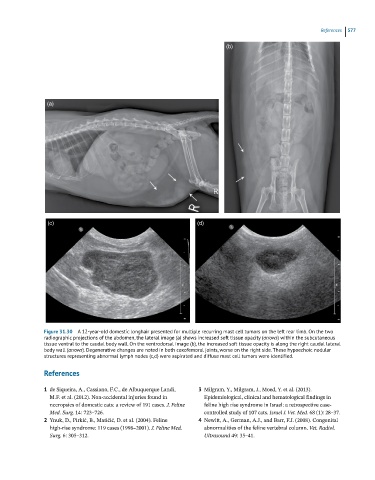
Figure 31.30 A 12-year-old domestic longhair presented for multiple recurring mast cell tumors on the left rear limb. On the two
radiographic projections of the abdomen, the lateral image (a) shows increased soft tissue opacity (arrows) within the subcutaneous
tissue ventral to the caudal body wall. On the ventrodorsal image (b), the increased soft tissue opacity is along the right caudal lateral
body wall (arrows). Degenerative changes are noted in both coxofemoral joints, worse on the right side. These hypoechoic nodular
structures representing abnormal lymph nodes (c,d) were aspirated and diffuse mast cell tumors were identified.
References
1 de Siqueira, A., Cassiano, F.C., de Albuquerque Landi, 3 Milgram, Y., Milgram, J., Moed, Y. et al. (2013).
M.F. et al. (2012). Non-accidental injuries found in Epidemiological, clinical and hematological findings in
necropsies of domestic cats: a review of 191 cases. J. Feline feline high rise syndrome in Israel: a retrospective case-
Med. Surg. 14: 723–726. controlled study of 107 cats. Israel J. Vet. Med. 68 (1): 28–37.
2 Ynuk, D., Pirkić, B., Matičić, D. et al. (2004). Feline 4 Newitt, A., German, A.J., and Barr, F.J. (2008). Congenital
high-rise syndrome: 119 cases (1998–2001). J. Feline Med. abnormalities of the feline vertebral column. Vet. Radiol.
Surg. 6: 305–312. Ultrasound 49: 35–41.