Page 1060 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1060
1032 PART VIII Reproductive System Disorders
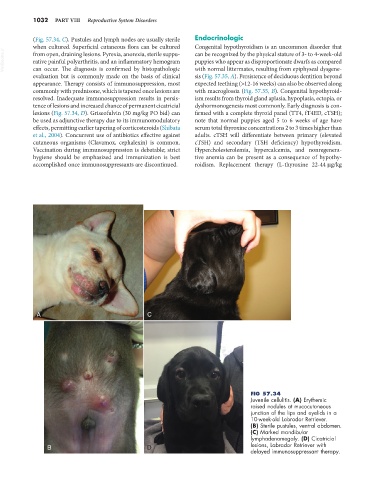
(Fig. 57.34, C). Pustules and lymph nodes are usually sterile Endocrinologic
when cultured. Superficial cutaneous flora can be cultured Congenital hypothyroidism is an uncommon disorder that
VetBooks.ir from open, draining lesions. Pyrexia, anorexia, sterile suppu- can be recognized by the physical stature of 3- to 4-week-old
puppies who appear as disproportionate dwarfs as compared
rative painful polyarthritis, and an inflammatory hemogram
can occur. The diagnosis is confirmed by histopathologic
sis (Fig. 57.35, A). Persistence of deciduous dentition beyond
evaluation but is commonly made on the basis of clinical with normal littermates, resulting from epiphyseal dysgene-
appearance. Therapy consists of immunosuppression, most expected teething (>12-16 weeks) can also be observed along
commonly with prednisone, which is tapered once lesions are with macroglossia (Fig. 57.35, B). Congenital hypothyroid-
resolved. Inadequate immunosuppression results in persis- ism results from thyroid gland aplasia, hypoplasia, ectopia, or
tence of lesions and increased chance of permanent cicatricial dyshormonogenesis most commonly. Early diagnosis is con-
lesions (Fig. 57.34, D). Griseofulvin (30 mg/kg PO bid) can firmed with a complete thyroid panel (TT4, fT4ED, cTSH);
be used as adjunctive therapy due to its immunomodulatory note that normal puppies aged 5 to 6 weeks of age have
effects, permitting earlier tapering of corticosteroids (Shibata serum total thyroxine concentrations 2 to 3 times higher than
et al., 2004). Concurrent use of antibiotics effective against adults. cTSH will differentiate between primary (elevated
cutaneous organisms (Clavamox, cephalexin) is common. cTSH) and secondary (TSH deficiency) hypothyroidism.
Vaccination during immunosuppression is debatable; strict Hypercholesterolemia, hypercalcemia, and nonregenera-
hygiene should be emphasized and immunization is best tive anemia can be present as a consequence of hypothy-
accomplished once immunosuppressants are discontinued. roidism. Replacement therapy (L-thyroxine 22-44 µg/kg
A C
FIG 57.34
Juvenile cellulitis. (A) Erythemic
raised nodules at mucocutaneous
junction of the lips and eyelids in a
10-week-old Labrador Retriever.
(B) Sterile pustules, ventral abdomen.
(C) Marked mandibular
lymphadenomegaly. (D) Cicatricial
B D lesions, Labrador Retriever with
delayed immunosuppressant therapy.