Page 1088 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1088
1060 PART IX Nervous System and Neuromuscular Disorders
VetBooks.ir
A B
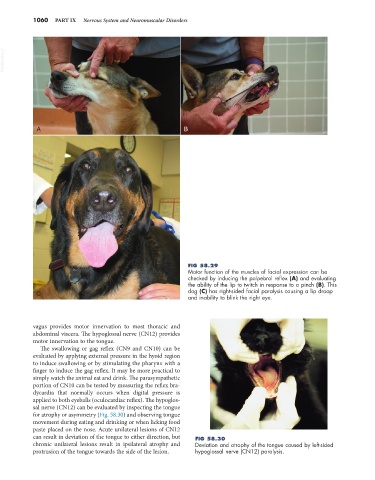
FIG 58.29
Motor function of the muscles of facial expression can be
checked by inducing the palpebral reflex (A) and evaluating
the ability of the lip to twitch in response to a pinch (B). This
C dog (C) has right-sided facial paralysis causing a lip droop
and inability to blink the right eye.
vagus provides motor innervation to most thoracic and
abdominal viscera. The hypoglossal nerve (CN12) provides
motor innervation to the tongue.
The swallowing or gag reflex (CN9 and CN10) can be
evaluated by applying external pressure in the hyoid region
to induce swallowing or by stimulating the pharynx with a
finger to induce the gag reflex. It may be more practical to
simply watch the animal eat and drink. The parasympathetic
portion of CN10 can be tested by measuring the reflex bra-
dycardia that normally occurs when digital pressure is
applied to both eyeballs (oculocardiac reflex). The hypoglos-
sal nerve (CN12) can be evaluated by inspecting the tongue
for atrophy or asymmetry (Fig. 58.30) and observing tongue
movement during eating and drinking or when licking food
paste placed on the nose. Acute unilateral lesions of CN12
can result in deviation of the tongue to either direction, but FIG 58.30
chronic unilateral lesions result in ipsilateral atrophy and Deviation and atrophy of the tongue caused by left-sided
protrusion of the tongue towards the side of the lesion. hypoglossal nerve (CN12) paralysis.