Page 1110 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1110
1082 PART IX Nervous System and Neuromuscular Disorders
VetBooks.ir
A B
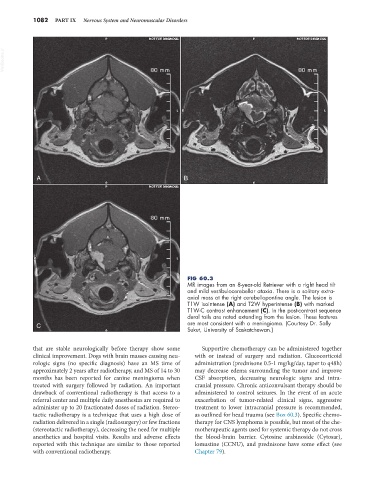
FIG 60.3
MR images from an 8-year-old Retriever with a right head tilt
and mild vestibulocerebellar ataxia. There is a solitary extra-
axial mass at the right cerebellopontine angle. The lesion is
T1W isointense (A) and T2W hyperintense (B) with marked
T1W-C contrast enhancement (C). In the post-contrast sequence
dural tails are noted extending from the lesion. These features
C are most consistent with a meningioma. (Courtesy Dr. Sally
Sukut, University of Saskatchewan.)
that are stable neurologically before therapy show some Supportive chemotherapy can be administered together
clinical improvement. Dogs with brain masses causing neu- with or instead of surgery and radiation. Glucocorticoid
rologic signs (no specific diagnosis) have an MS time of administration (prednisone 0.5-1 mg/kg/day, taper to q48h)
approximately 2 years after radiotherapy, and MS of 14 to 30 may decrease edema surrounding the tumor and improve
months has been reported for canine meningioma when CSF absorption, decreasing neurologic signs and intra-
treated with surgery followed by radiation. An important cranial pressure. Chronic anticonvulsant therapy should be
drawback of conventional radiotherapy is that access to a administered to control seizures. In the event of an acute
referral center and multiple daily anesthesias are required to exacerbation of tumor-related clinical signs, aggressive
administer up to 20 fractionated doses of radiation. Stereo- treatment to lower intracranial pressure is recommended,
tactic radiotherapy is a technique that uses a high dose of as outlined for head trauma (see Box 60.3). Specific chemo-
radiation delivered in a single (radiosurgery) or few fractions therapy for CNS lymphoma is possible, but most of the che-
(stereotactic radiotherapy), decreasing the need for multiple motherapeutic agents used for systemic therapy do not cross
anesthetics and hospital visits. Results and adverse effects the blood-brain barrier. Cytosine arabinoside (Cytosar),
reported with this technique are similar to those reported lomustine (CCNU), and prednisone have some effect (see
with conventional radiotherapy. Chapter 79).