Page 1113 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1113
CHAPTER 61 Loss of Vision and Pupillary Abnormalities 1085
BOX 61.1
VetBooks.ir Lesions Causing Loss of the Menace Response in Dogs
and Cats
Severe ocular disease
Retinal disease
Visual pathway lesion
Retina Ipsilateral optic nerve
Optic chiasm
Optic nerve Contralateral optic tract, lateral geniculate nucleus,
optic radiation
Optic chiasm
Contralateral visual cortex (forebrain) lesion
Optic tract Altered mental status
Lateral geniculate Metabolic encephalopathy
nucleus Severe systemic illness
Optic radiations Cerebellar disease
Inability to blink (CN7)
Occipital (visual) cortex Immature reflex (<12 weeks of age)
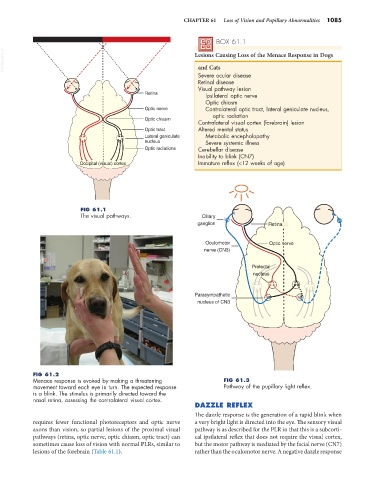
FIG 61.1
The visual pathways. Ciliary
ganglion Retina
Oculomotor Optic nerve
nerve (CN3)
Pretectal
nucleus
Parasympathetic
nucleus of CN3
FIG 61.2
Menace response is evoked by making a threatening FIG 61.3
movement toward each eye in turn. The expected response Pathway of the pupillary light reflex.
is a blink. The stimulus is primarily directed toward the
nasal retina, assessing the contralateral visual cortex.
DAZZLE REFLEX
The dazzle response is the generation of a rapid blink when
requires fewer functional photoreceptors and optic nerve a very bright light is directed into the eye. The sensory visual
axons than vision, so partial lesions of the proximal visual pathway is as described for the PLR in that this is a subcorti-
pathways (retina, optic nerve, optic chiasm, optic tract) can cal ipsilateral reflex that does not require the visual cortex,
sometimes cause loss of vision with normal PLRs, similar to but the motor pathway is mediated by the facial nerve (CN7)
lesions of the forebrain (Table 61.1). rather than the oculomotor nerve. A negative dazzle response