Page 1117 - Small Animal Internal Medicine, 6th Edition
P. 1117
CHAPTER 61 Loss of Vision and Pupillary Abnormalities 1089
VetBooks.ir
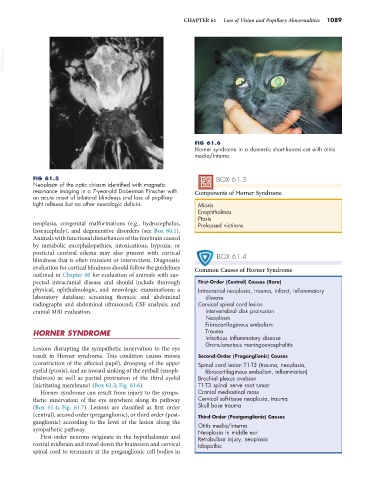
FIG 61.6
Horner syndrome in a domestic short-haired cat with otitis
media/interna.
FIG 61.5 BOX 61.3
Neoplasm of the optic chiasm identified with magnetic
resonance imaging in a 7-year-old Doberman Pinscher with Components of Horner Syndrome
an acute onset of bilateral blindness and loss of pupillary
light reflexes but no other neurologic deficits. Miosis
Enophthalmos
Ptosis
neoplasia, congenital malformations (e.g., hydrocephalus, Prolapsed nictitans
lissencephaly), and degenerative disorders (see Box 60.1).
Animals with functional disturbances of the forebrain caused
by metabolic encephalopathies, intoxications, hypoxia, or
postictal cerebral edema may also present with cortical BOX 61.4
blindness that is often transient or intermittent. Diagnostic
evaluation for cortical blindness should follow the guidelines Common Causes of Horner Syndrome
outlined in Chapter 60 for evaluation of animals with sus-
pected intracranial disease and should include thorough First-Order (Central) Causes (Rare)
physical, ophthalmologic, and neurologic examinations; a Intracranial neoplasia, trauma, infarct, inflammatory
laboratory database; screening thoracic and abdominal disease
radiographs and abdominal ultrasound; CSF analysis; and Cervical spinal cord lesion
cranial MRI evaluation. Intervertebral disk protrusion
Neoplasm
Fibrocartilaginous embolism
HORNER SYNDROME Trauma
Infectious inflammatory disease
Granulomatous meningoencephalitis
Lesions disrupting the sympathetic innervation to the eye
result in Horner syndrome. This condition causes miosis Second-Order (Preganglionic) Causes
(constriction of the affected pupil), drooping of the upper Spinal cord lesion T1-T3 (trauma, neoplasia,
eyelid (ptosis), and an inward sinking of the eyeball (enoph- fibrocartilaginous embolism, inflammation)
thalmos) as well as partial protrusion of the third eyelid Brachial plexus avulsion
(nictitating membrane) (Box 61.3; Fig. 61.6). T1-T3 spinal nerve root tumor
Horner syndrome can result from injury to the sympa- Cranial mediastinal mass
thetic innervation of the eye anywhere along its pathway Cervical soft-tissue neoplasia, trauma
(Box 61.4; Fig. 61.7). Lesions are classified as first order Skull base trauma
(central), second order (preganglionic), or third order (post- Third-Order (Postganglionic) Causes
ganglionic) according to the level of the lesion along the Otitis media/interna
sympathetic pathway. Neoplasia in middle ear
First-order neurons originate in the hypothalamus and Retrobulbar injury, neoplasia
rostral midbrain and travel down the brainstem and cervical Idiopathic
spinal cord to terminate at the preganglionic cell bodies in