Page 408 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 408
Pathology/cytology 377
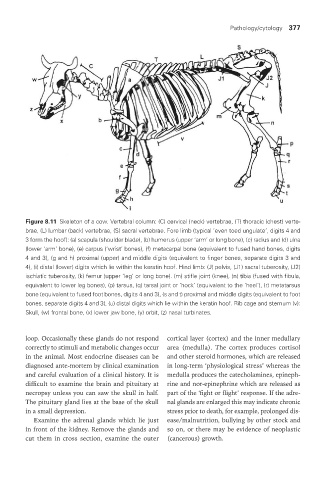
Figure 8.11 Skeleton of a cow. Vertebral column: (C) cervical (neck) vertebrae, (T) thoracic (chest) verte-
brae, (L) lumbar (back) vertebrae, (S) sacral vertebrae. Fore limb (typical ‘even toed ungulate’, digits 4 and
3 form the hoof): (a) scapula (shoulder blade), (b) humerus (upper ‘arm’ or long bone), (c) radius and (d) ulna
(lower ‘arm’ bone), (e) carpus (‘wrist’ bones), (f) metacarpal bone (equivalent to fused hand bones, digits
4 and 3), (g and h) proximal (upper) and middle digits (equivalent to finger bones, separate digits 3 and
4), (i) distal (lower) digits which lie within the keratin hoof. Hind limb: (J) pelvis, (J1) sacral tuberosity, (J2)
ischiatic tuberosity, (k) femur (upper ‘leg’ or long bone). (m) stifle joint (knee), (n) tibia (fused with fibula,
equivalent to lower leg bones), (p) tarsus, (q) tarsal joint or ‘hock’ (equivalent to the ‘heel’), (r) metatarsus
bone (equivalent to fused foot bones, digits 4 and 3), (s and t) proximal and middle digits (equivalent to foot
bones, separate digits 4 and 3), (u) distal digits which lie within the keratin hoof. Rib cage and sternum (v):
Skull, (w) frontal bone, (x) lower jaw bone, (y) orbit, (z) nasal turbinates.
loop. Occasionally these glands do not respond cortical layer (cortex) and the inner medullary
correctly to stimuli and metabolic changes occur area (medulla). The cortex produces cortisol
in the animal. Most endocrine diseases can be and other steroid hormones, which are released
diagnosed ante-mortem by clinical examination in long-term ‘physiological stress’ whereas the
and careful evaluation of a clinical history. It is medulla produces the catecholamines, epineph-
difficult to examine the brain and pituitary at rine and nor-epinephrine which are released as
necropsy unless you can saw the skull in half. part of the ‘fight or flight’ response. If the adre-
The pituitary gland lies at the base of the skull nal glands are enlarged this may indicate chronic
in a small depression. stress prior to death, for example, prolonged dis-
Examine the adrenal glands which lie just ease/malnutrition, bullying by other stock and
in front of the kidney. Remove the glands and so on, or there may be evidence of neoplastic
cut them in cross section, examine the outer (cancerous) growth.
Vet Lab.indb 377 26/03/2019 10:26