Page 405 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 405
374 Susan C. Cork
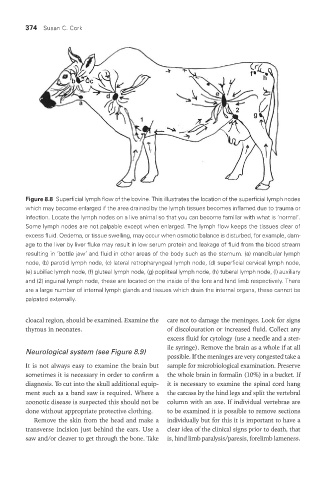
Figure 8.8 Superficial lymph flow of the bovine. This illustrates the location of the superficial lymph nodes
which may become enlarged if the area drained by the lymph tissues becomes inflamed due to trauma or
infection. Locate the lymph nodes on a live animal so that you can become familiar with what is ‘normal’.
Some lymph nodes are not palpable except when enlarged. The lymph flow keeps the tissues clear of
excess fluid. Oedema, or tissue swelling, may occur when osmotic balance is disturbed, for example, dam-
age to the liver by liver fluke may result in low serum protein and leakage of fluid from the blood stream
resulting in ‘bottle jaw’ and fluid in other areas of the body such as the sternum. (a) mandibular lymph
node, (b) parotid lymph node, (c) lateral retropharyngeal lymph node, (d) superficial cervical lymph node,
(e) subiliac lymph node, (f) gluteal lymph node, (g) popliteal lymph node, (h) tuberal lymph node, (l) auxiliary
and (2) inguinal lymph node, these are located on the inside of the fore and hind limb respectively. There
are a large number of internal lymph glands and tissues which drain the internal organs, these cannot be
palpated externally.
cloacal region, should be examined. Examine the care not to damage the meninges. Look for signs
thymus in neonates. of discolouration or increased fluid. Collect any
excess fluid for cytology (use a needle and a ster-
ile syringe). Remove the brain as a whole if at all
Neurological system (see Figure 8.9)
possible. If the meninges are very congested take a
It is not always easy to examine the brain but sample for microbiological examination. Preserve
sometimes it is necessary in order to confirm a the whole brain in formalin (10%) in a bucket. If
diagnosis. To cut into the skull additional equip- it is necessary to examine the spinal cord hang
ment such as a band saw is required. Where a the carcass by the hind legs and split the vertebral
zoonotic disease is suspected this should not be column with an axe. If individual vertebrae are
done without appropriate protective clothing. to be examined it is possible to remove sections
Remove the skin from the head and make a individually but for this it is important to have a
transverse incision just behind the ears. Use a clear idea of the clinical signs prior to death, that
saw and/or cleaver to get through the bone. Take is, hind limb paralysis/paresis, forelimb lameness.
Vet Lab.indb 374 26/03/2019 10:26