Page 402 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 402
Pathology/cytology 371
A B
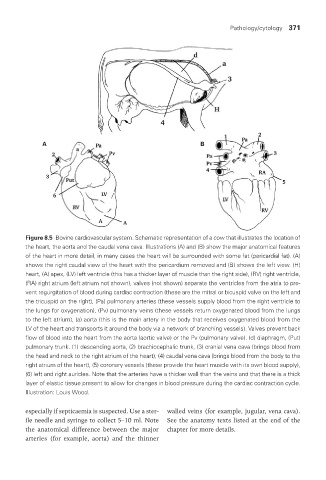
Figure 8.5 Bovine cardiovascular system. Schematic representation of a cow that illustrates the location of
the heart, the aorta and the caudal vena cava. Illustrations (A) and (B) show the major anatomical features
of the heart in more detail, in many cases the heart will be surrounded with some fat (pericardial fat). (A)
shows the right caudal view of the heart with the pericardium removed and (B) shows the left view. (H)
heart, (A) apex, (LV) left ventricle (this has a thicker layer of muscle than the right side), (RV) right ventricle,
(RA) right atrium (left atrium not shown), valves (not shown) separate the ventricles from the atria to pre-
vent regurgitation of blood during cardiac contraction (these are the mitral or bicuspid valve on the left and
the tricuspid on the right), (Pa) pulmonary arteries (these vessels supply blood from the right ventricle to
the lungs for oxygenation), (Pv) pulmonary veins (these vessels return oxygenated blood from the lungs
to the left atrium), (a) aorta (this is the main artery in the body that receives oxygenated blood from the
LV of the heart and transports it around the body via a network of branching vessels). Valves prevent back
flow of blood into the heart from the aorta (aortic valve) or the Pv (pulmonary valve). (d) diaphragm, (Put)
pulmonary trunk. (1) descending aorta, (2) brachiocephalic trunk, (3) cranial vena cava (brings blood from
the head and neck to the right atrium of the heart), (4) caudal vena cava (brings blood from the body to the
right atrium of the heart), (5) coronary vessels (these provide the heart muscle with its own blood supply),
(6) left and right auricles. Note that the arteries have a thicker wall than the veins and that there is a thick
layer of elastic tissue present to allow for changes in blood pressure during the cardiac contraction cycle.
Illustration: Louis Wood.
especially if septicaemia is suspected. Use a ster- walled veins (for example, jugular, vena cava).
ile needle and syringe to collect 5–10 ml. Note See the anatomy texts listed at the end of the
the anatomical difference between the major chapter for more details.
arteries (for example, aorta) and the thinner
Vet Lab.indb 371 26/03/2019 10:26