Page 404 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 404
Pathology/cytology 373
Examine the throat and trachea for signs
of obstruction and/or inflammatory changes.
Examine the thoracic cavity for evidence of
trauma.
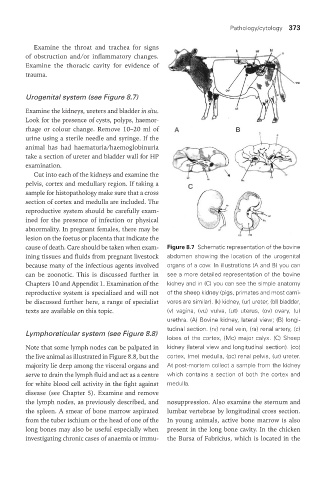
Urogenital system (see Figure 8.7)
Examine the kidneys, ureters and bladder in situ.
Look for the presence of cysts, polyps, haemor-
rhage or colour change. Remove 10–20 ml of
urine using a sterile needle and syringe. If the
animal has had haematuria/haemoglobinuria
take a section of ureter and bladder wall for HP
examination.
Cut into each of the kidneys and examine the
pelvis, cortex and medullary region. If taking a
sample for histopathology make sure that a cross
section of cortex and medulla are included. The
reproductive system should be carefully exam-
ined for the presence of infection or physical
abnormality. In pregnant females, there may be
lesion on the foetus or placenta that indicate the
cause of death. Care should be taken when exam- Figure 8.7 Schematic representation of the bovine
ining tissues and fluids from pregnant livestock abdomen showing the location of the urogenital
because many of the infectious agents involved organs of a cow. In illustrations (A and B) you can
can be zoonotic. This is discussed further in see a more detailed representation of the bovine
Chapters 10 and Appendix 1. Examination of the kidney and in (C) you can see the simple anatomy
reproductive system is specialized and will not of the sheep kidney (pigs, primates and most carni-
be discussed further here, a range of specialist vores are similar). (k) kidney, (ur) ureter, (bl) bladder,
texts are available on this topic. (v) vagina, (vu) vulva, (ut) uterus, (ov) ovary, (u)
urethra. (A) Bovine kidney, lateral view; (B) longi-
tudinal section. (rv) renal vein, (ra) renal artery, (c)
Lymphoreticular system (see Figure 8.8)
lobes of the cortex, (Mc) major calyx. (C) Sheep
Note that some lymph nodes can be palpated in kidney (lateral view and longitudinal section). (co)
the live animal as illustrated in Figure 8.8, but the cortex, (me) medulla, (pc) renal pelvis, (ur) ureter.
majority lie deep among the visceral organs and At post-mortem collect a sample from the kidney
serve to drain the lymph fluid and act as a centre which contains a section of both the cortex and
for white blood cell activity in the fight against medulla.
disease (see Chapter 5). Examine and remove
the lymph nodes, as previously described, and nosuppression. Also examine the sternum and
the spleen. A smear of bone marrow aspirated lumbar vertebrae by longitudinal cross section.
from the tuber ischium or the head of one of the In young animals, active bone marrow is also
long bones may also be useful especially when present in the long bone cavity. In the chicken
investigating chronic cases of anaemia or immu- the Bursa of Fabricius, which is located in the
Vet Lab.indb 373 26/03/2019 10:26