Page 427 - The Veterinary Laboratory and Field Manual 3rd Edition
P. 427
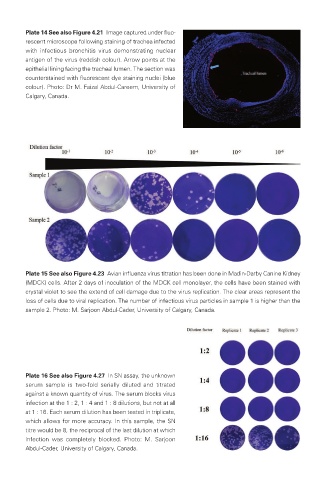
Plate 14 See also Figure 4.21 Image captured under fluo-
rescent microscope following staining of trachea infected
with infectious bronchitis virus demonstrating nuclear
antigen of the virus (reddish colour). Arrow points at the
epithelial lining facing the tracheal lumen. The section was
counterstained with fluorescent dye staining nuclei (blue
colour). Photo: Dr M. Faizal Abdul-Careem, University of
Calgary, Canada.
Plate 15 See also Figure 4.23 Avian influenza virus titration has been done in Madin-Darby Canine Kidney
(MDCK) cells. After 2 days of inoculation of the MDCK cell monolayer, the cells have been stained with
crystal violet to see the extend of cell damage due to the virus replication. The clear areas represent the
loss of cells due to viral replication. The number of infectious virus particles in sample 1 is higher than the
sample 2. Photo: M. Sarjoon Abdul-Cader, University of Calgary, Canada.
Plate 16 See also Figure 4.27 In SN assay, the unknown
serum sample is two-fold serially diluted and titrated
against a known quantity of virus. The serum blocks virus
infection at the 1 : 2, 1 : 4 and 1 : 8 dilutions, but not at all
at 1 : 16. Each serum dilution has been tested in triplicate,
which allows for more accuracy. In this sample, the SN
titre would be 8, the reciprocal of the last dilution at which
infection was completely blocked. Photo: M. Sarjoon
Abdul-Cader, University of Calgary, Canada.
Veterinary-plates.indd 10 26/03/2019 10:14