Page 476 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 476
442 Chapter 4
collagen fibers in the DDFT and fissuring of the fibro-
cartilage on the flexor surface of the navicular bone. 33,134
VetBooks.ir lation may predispose to adhesion formation between
Damage to the fibrocartilage together with DDFT fibril-
the tendon and the bone. Other studies have identified
superficial or deep sagittal or parasagittal crevices or
splits of the DDFT, abrasions or fibrillation on the dor-
sal surface, focal fibrocartilaginous metaplasia, and
focal fibroplasia (Figure 4.5). 10,96 These abnormalities
were not related to age, but lesions on the dorsal aspect
of the DDFT were significantly more common in lame
horses than control horses. In addition, true core
11
lesions appeared to be uncommon, and there was little
evidence of acute inflammatory changes within the
DDFT. Superficial lesions on the dorsal surface of the
10
DDFT may occur without detectable lameness, but
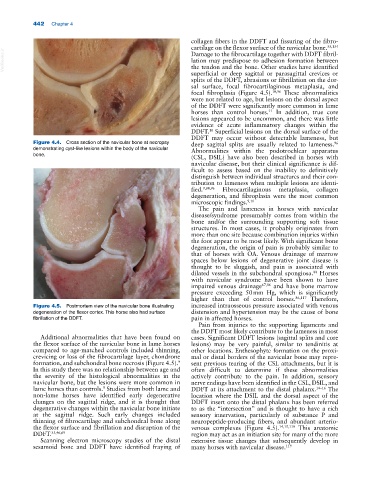
Figure 4.4. Cross section of the navicular bone at necropsy deep sagittal splits are usually related to lameness.
96
demonstrating cyst‐like lesions within the body of the navicular Abnormalities within the podotrochlear apparatus
bone. (CSL, DSIL) have also been described in horses with
navicular disease, but their clinical significance is dif-
ficult to assess based on the inability to definitively
distinguish between individual structures and their con-
tribution to lameness when multiple lesions are identi-
fied. 9,84,96 Fibrocartilaginous metaplasia, collagen
degeneration, and fibroplasia were the most common
microscopic findings. 9,10
The pain and lameness in horses with navicular
disease/syndrome presumably comes from within the
bone and/or the surrounding supporting soft tissue
structures. In most cases, it probably originates from
more than one site because combination injuries within
the foot appear to be most likely. With significant bone
degeneration, the origin of pain is probably similar to
that of horses with OA. Venous drainage of marrow
spaces below lesions of degenerative joint disease is
thought to be sluggish, and pain is associated with
dilated vessels in the subchondral spongiosa. Horses
88
with navicular syndrome have been shown to have
impaired venous drainage 67,86 and have bone marrow
pressure exceeding 50 mm Hg, which is significantly
higher than that of control horses. 86,117 Therefore,
Figure 4.5. Postmortem view of the navicular bone illustrating increased intraosseous pressure associated with venous
degeneration of the flexor cortex. This horse also had surface distension and hypertension may be the cause of bone
fibrillation of the DDFT. pain in affected horses.
Pain from injuries to the supporting ligaments and
the DDFT most likely contribute to the lameness in most
Additional abnormalities that have been found on cases. Significant DDFT lesions (sagittal splits and core
the flexor surface of the navicular bone in lame horses lesions) may be very painful, similar to tendinitis at
compared to age‐matched controls included thinning, other locations. Enthesophyte formation on the proxi-
crevicing or loss of the fibrocartilage layer, chondrone mal or distal borders of the navicular bone may repre-
formation, and subchondral bone necrosis (Figure 4.5). sent previous tearing of the CSL attachments, but it is
9
In this study there was no relationship between age and often difficult to determine if these abnormalities
the severity of the histological abnormalities in the actively contribute to the pain. In addition, sensory
navicular bone, but the lesions were more common in nerve endings have been identified in the CSL, DSIL, and
lame horses than controls. Studies from both lame and DDFT at its attachment to the distal phalanx. 14–16 The
9
non‐lame horses have identified early degenerative location where the DSIL and the dorsal aspect of the
changes on the sagittal ridge, and it is thought that DDFT insert onto the distal phalanx has been referred
degenerative changes within the navicular bone initiate to as the “intersection” and is thought to have a rich
at the sagittal ridge. Such early changes included sensory innervation, particularly of substance P and
thinning of fibrocartilage and subchondral bone along neuropeptide‐producing fibers, and abundant arterio-
the flexor surface and fibrillation and disruption of the venous complexes (Figure 4.5). 14,15,119 This anatomic
DDFT. 35,46,69 region may act as an initiation site for many of the more
Scanning electron microscopy studies of the distal extensive tissue changes that subsequently develop in
sesamoid bone and DDFT have identified fraying of many horses with navicular disease. 119