Page 824 - Adams and Stashak's Lameness in Horses, 7th Edition
P. 824
790 Chapter 6
VetBooks.ir
Figure 6.34. Ultrasonographic images of the lumbar spine. Right side, two longitudinal paramedian views. The respective facet
Transverse views (left images) of the left side and right side; the joints are seen in the circles; the joint space and both facets are in
facet joint surfaces and the joint spaces are seen in the circles. the left circle, and in the right circle the joint space is not visible.
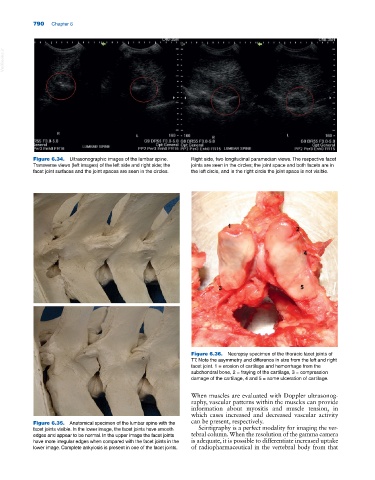
Figure 6.36. Necropsy specimen of the thoracic facet joints of
T7. Note the asymmetry and difference in size from the left and right
facet joint. 1 = erosion of cartilage and hemorrhage from the
subchondral bone, 2 = fraying of the cartilage, 3 = compression
damage of the cartilage, 4 and 5 = some ulceration of cartilage.
When muscles are evaluated with Doppler ultrasonog-
raphy, vascular patterns within the muscles can provide
information about myositis and muscle tension, in
which cases increased and decreased vascular activity
Figure 6.35. Anatomical specimen of the lumbar spine with the can be present, respectively.
facet joints visible. In the lower image, the facet joints have smooth Scintigraphy is a perfect modality for imaging the ver-
edges and appear to be normal. In the upper image the facet joints tebral column. When the resolution of the gamma camera
have more irregular edges when compared with the facet joints in the is adequate, it is possible to differentiate increased uptake
lower image. Complete ankylosis is present in one of the facet joints. of radiopharmaceutical in the vertebral body from that