Page 241 - Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals, 8th Edition
P. 241
226 / Anatomy and Physiology of Farm Animals
fibers of the iris which constrict the pupil. neurons (see Chapter 10), and these cells
release their hormones when stimulated.
Other examples include: the production of
VetBooks.ir tears in response to stimulating the sur In most species epinephrine is the primary
substance released by chromaffin cells.
face of the eye; vasoconstriction of blood
vessels in response to low blood pressure; Epinephrine and norepinephrine in the
or contraction of the gut in response to circulation bind to adrenergic receptors
stretch in the wall. Most autonomic func throughout the body to amplify the general
tions can be understood in terms of a effects of increased sympathetic nerve
reflex arc (in other words, an autonomic activity. When animals are not undergoing
response to some measurable body state), the fight‐or‐flight response, the blood levels
although some of these are very complex. of these hormones are relatively low and
As described above, the sympathetic functionally insignificant.
division of the ANS is activated when the
body needs to meet some physical demand. Autonomic Neurotransmitters
It is also the arm of the ANS that domi and Their Receptors
nates when strong emotional states like
fear or anger are experienced. Under The postganglionic neurons of the parasym
these conditions, a generalized activation pathetic division of the ANS release ACh as
of sympathetic effects called the “fight‐ their neurotransmitter, whereas almost all
or‐flight” response can occur. The fight‐or‐ postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic
flight response is a state characterized by division release norepinephrine. ACh is also
high levels of sympathetic activity through the neurotransmitter used by preganglionic
out the body. This widespread sympathetic neurons in both the sympathetic and para
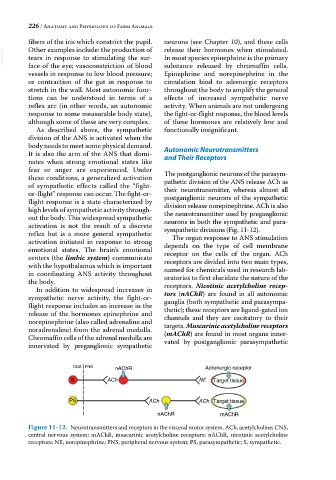
activation is not the result of a discrete sympathetic divisions (Fig. 11‐12).
reflex but is a more general sympathetic The organ response to ANS stimulation
activation initiated in response to strong depends on the type of cell membrane
emotional states. The brain’s emotional receptor on the cells of the organ. ACh
centers (the limbic system) communicate receptors are divided into two main types,
with the hypothalamus which is important named for chemicals used in research lab
in coordinating ANS activity throughout oratories to first elucidate the nature of the
the body.
In addition to widespread increases in receptors. Nicotinic acetylcholine recep-
sympathetic nerve activity, the fight‐or‐ tors (nAChR) are found in all autonomic
ganglia (both sympathetic and parasympa
flight response includes an increase in the thetic); these receptors are ligand‐gated ion
release of the hormones epinephrine and channels and they are excitatory to their
norepinephrine (also called adrenaline and targets. Muscarinic acetylcholine receptors
noradrenaline) from the adrenal medulla. (mAChR) are found in most organs inner
Chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla are vated by postganglionic parasympathetic
innervated by preganglionic sympathetic
CNS PNS nAChR Adrenergic receptor
S ACh NE Target tissue
PS ACh ACh Target tissue
nAChR mAChR
Figure 11-12. Neurotransmitters and receptors in the visceral motor system. ACh, acetylcholine; CNS,
central nervous system; mAChR, muscarinic acetylcholine receptors; nAChR, nicotinic acetylcholine
receptors; NE, norepinephrine; PNS, peripheral nervous system; PS, parasympathetic; S, sympathetic.