Page 187 - Clinical Small Animal Internal Medicine
P. 187
16 Imaging in Cardiovascular Disease 155
VetBooks.ir (a): healthy dog regurgitation
Pulmonary
(b): dog with PAH
(c): dog with PAH
Pulmonary regurgitation
3.2 m/s
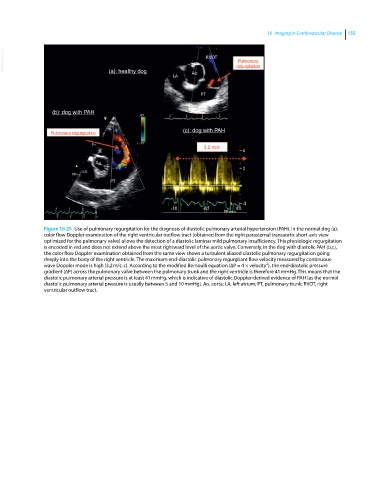
Figure 16.25 Use of pulmonary regurgitation for the diagnosis of diastolic pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH). In the normal dog (a),
color flow Doppler examination of the right ventricular outflow tract (obtained from the right parasternal transaortic short‐axis view
optimized for the pulmonary valve) allows the detection of a diastolic laminar mild pulmonary insufficiency. This physiologic regurgitation
is encoded in red and does not extend above the most rightward level of the aortic valve. Conversely, in the dog with diastolic PAH (b,c),
the color flow Doppler examination obtained from the same view shows a turbulent aliased diastolic pulmonary regurgitation going
deeply into the body of the right ventricle. The maximum end‐diastolic pulmonary regurgitant flow velocity measured by continuous‐
2
wave Doppler mode is high (3.2 m/s; c). According to the modified Bernoulli equation (∆P = 4 × velocity ), the end‐diastolic pressure
gradient (∆P) across the pulmonary valve between the pulmonary trunk and the right ventricle is therefore 41 mmHg. This means that the
diastolic pulmonary arterial pressure is at least 41 mmHg, which is indicative of diastolic Doppler‐derived evidence of PAH (as the normal
diastolic pulmonary arterial pressure is usually between 5 and 10 mmHg). Ao, aorta; LA, left atrium; PT, pulmonary trunk; RVOT, right
ventricular outflow tract.