Page 21 - pulse 2019 issue 3
P. 21
in 2012 infected 2,494 individuals with when a reproductive number is below 1.
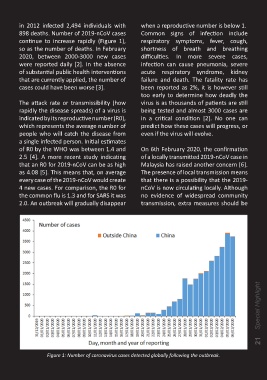
898 deaths. Number of 2019-nCoV cases Common signs of infection include
continue to increase rapidly (Figure 1), respiratory symptoms, fever, cough,
so as the number of deaths. In February shortness of breath and breathing
2020, between 2000-3000 new cases difficulties. In more severe cases,
were reported daily [2]. In the absence infection can cause pneumonia, severe
of substantial public health interventions acute respiratory syndrome, kidney
that are currently applied, the number of failure and death. The fatality rate has
cases could have been worse [3]. been reported as 2%, it is however still
too early to determine how deadly the
The attack rate or transmissibility (how virus is as thousands of patients are still
rapidly the disease spreads) of a virus is being tested and almost 3000 cases are
indicated by its reproductive number (R0), in a critical condition [2]. No one can
which represents the average number of predict how these cases will progress, or
people who will catch the disease from even if the virus will evolve.
a single infected person. Initial estimates
of R0 by the WHO was between 1.4 and On 6th February 2020, the confirmation
2.5 [4]. A more recent study indicating of a locally transmitted 2019-nCoV case in
that an R0 for 2019-nCoV can be as high Malaysia has raised another concern [6].
as 4.08 [5]. This means that, on average The presence of local transmission means
every case of the 2019-nCoV would create that there is a possibility that the 2019-
4 new cases. For comparison, the R0 for nCoV is now circulating locally. Although
the common flu is 1.3 and for SARS it was no evidence of widespread community
2.0. An outbreak will gradually disappear transmission, extra measures should be
Special Highlight
21
Figure 1: Number of coronavirus cases detected globally following the outbreak.