Page 169 - Essential Haematology
P. 169
Chapter 11 Haematological malignancy: aetiology and genetics / 155
control of apoptosis (e.g. BCL - 2 which is overex- 11.4 ). Tumour - suppressor genes commonly act as
pressed in follicular lymphoma) (see p. 266 ). components of control mechanisms that regulate
entry of the cell from the G 1 phase of the cell cycle
into the S phase or passage through the S phase to
Tyrosine k inases
G 2 and mitosis (see Fig. 1.8 ). Examples of onco-
These enzymes, which phosphorylate proteins on genes and tumour - suppressor genes involved in
tyrosine residues, are important as cell receptors and haemopoietic malignancies are shown in Table
intracellular signalling. Mutations of them underlie 11.1 . The most significant tumour - suppressor gene
a large number of haematological malignancies (see in human cancer is p53 which is mutated or inac-
Chapters 13 , 14 and 15 ). tivated in over 50% of cases of malignant disease,
including many haemopoietic tumours.
Tumour - s uppressor g enes
Clonal p rogression
Tumour - suppressor genes may acquire loss - of - func-
tion mutations, usually by point mutation or dele- Malignant cells appear to arise as a multistep process
tion, which lead to malignant transformation (Fig. with acquisition of mutations in diff erent intracel-
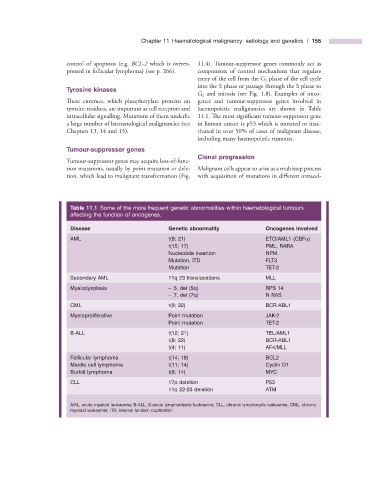
Table 11.1 Some of the more frequent genetic abnormalities within haematological tumours
affecting the function of oncogenes.
Disease Genetic abnormality Oncogenes involved
AML t(8; 21) ETO/AML1 (CBF α )
t(15; 17) PML, RARA
Nucleotide insertion NPM
Mutation, ITD FLT3
Mutation TET - 2
Secondary AML 11q 23 translocations MLL
Myelodysplasia – 5, del (5q) RPS 14
– 7, del (7q) N RAS
CML t(9; 22) BCR - ABL1
Myeloproliferative Point mutation JAK - 2
Point mutation TET - 2
B - ALL t(12; 21) TEL/AML1
t(9; 22) BCR - ABL1
t(4; 11) AF4/MLL
Follicular lymphoma t(14; 18) BCL2
Mantle cell lymphoma t(11; 14) Cyclin D1
Burkitt lymphoma t(8; 14) MYC
CLL 17p deletion P53
11q 22 - 23 deletion ATM
AML, acute myeloid leukaemia; B - ALL, B - acute lymphoblastic leukaemia; CLL, chronic lymphocytic leukaemia; CML, chronic
myeloid leukaemia ; ITD, internal tandem duplication.