Page 173 - Essential Haematology
P. 173
Chapter 11 Haematological malignancy: aetiology and genetics / 159
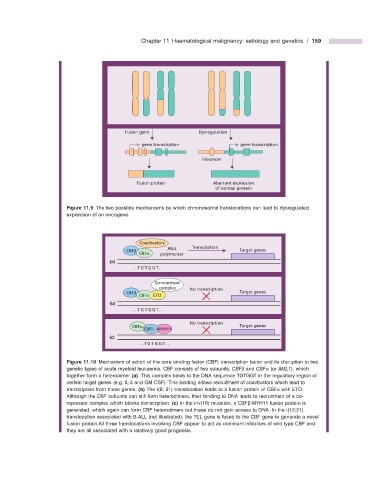
Fusion gene Dysregulation
gene transcription gene transcription
Enhancer
Fusion protein Aberrant expression
of normal protein
Figure 11.9 The two possible mechanisms by which chromosomal translocations can lead to dysregulated
expression of an oncogene.
Coactivators
CBFβ RNA Transcription Target genes
CBFα polymerase
(a)
..TGTGGT..
Co-repressor
complex No transcription
CBFβ Target genes
CBFα ETO
(b)
..TGTGGT..
No transcription
CBFα Target genes
CBFβ- MYH11
(c)
..TGTGGT..
Figure 11.10 Mechanism of action of the core binding factor (CBF) transcription factor and its disruption in two
genetic types of acute myeloid leukaemia. CBF consists of two subunits, CBF β and CBF α (or AML1 ), which
together form a heterodimer (a) . This complex binds to the DNA sequence TGTGGT in the regulatory region of
certain target genes (e.g. IL - 3 and GM - CSF). This binding allows recruitment of coactivators which lead to
transcription from these genes. (b) The t(8; 21) translocation leads to a fusion protein of CBF α with ETO.
Although the CBF subunits can still form heterodimers, their binding to DNA leads to recruitment of a co -
repressor complex which blocks transcription. (c) In the inv(16) mutation, a CBF β - MYH11 fusion protein is
generated, which again can form CBF heterodimers but these do not gain access to DNA. In the t(12;21)
translocation associated with B - ALL (not illustrated), the TEL gene is fused to the CBF gene to generate a novel
fusion protein.All three translocations involving CBF appear to act as dominant inhibitors of wild type CBF and
they are all associated with a relatively good prognosis.