Page 175 - Essential Haematology
P. 175
Chapter 11 Haematological malignancy: aetiology and genetics / 161
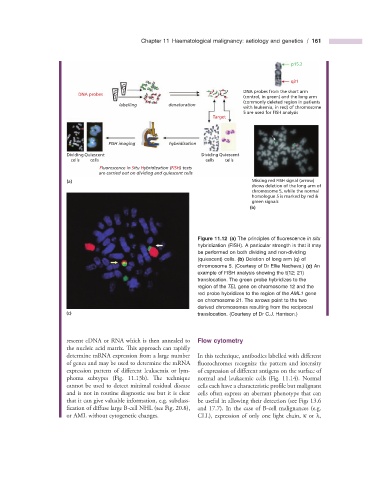
p15.2
q31
DNA probes from the short arm
DNA probes
(control, in green) and the long arm
(commonly deleted region in patients
labelling denaturation
with leukemia, in red) of chromosome
5 are used for FISH analysis
Target
FISH imaging hybridization
Dividing Quiescent Dividing Quiescent
cells cells cells cells
Fluorescence In Situ Hybridization (FISH) tests
are carried out on dividing and quiescent cells
(a) Missing red FISH signal (arrow)
shows deletion of the long arm of
chromosome 5, while the normal
homologue 5 is marked by red &
green signals
(b)
Figure 11.12 (a) The principles of fl uorescence in situ
hybridization (FISH). A particular strength is that it may
be performed on both dividing and non - dividing
(quiescent) cells. (b) Deletion of long arm (q) of
chromosome 5. (Courtesy of Dr Ellie Nacheva.) (c) An
example of FISH analysis showing the t(12; 21)
translocation. The green probe hybridizes to the
region of the TEL gene on chromosome 12 and the
red probe hybridizes to the region of the AML1 gene
on chromosome 21. The arrows point to the two
derived chromosomes resulting from the reciprocal
(c) translocation. (Courtesy of Dr C.J. Harrison.)
rescent cDNA or RNA which is then annealed to Flow c ytometry
the nucleic acid matrix. This approach can rapidly
determine mRNA expression from a large number In this technique, antibodies labelled with diff erent
of genes and may be used to determine the mRNA fl uorochromes recognize the pattern and intensity
expression pattern of different leukaemia or lym- of expression of different antigens on the surface of
phoma subtypes (Fig. 11.13 b). Th e technique normal and leukaemic cells (Fig. 11.14 ). Normal
cannot be used to detect minimal residual disease cells each have a characteristic profi le but malignant
and is not in routine diagnostic use but it is clear cells often express an aberrant phenotype that can
that it can give valuable information, e.g. subclass- be useful in allowing their detection (see Figs 13.6
fication of diffuse large B - cell NHL (see Fig. 20.8 ), and 17.7 ). In the case of B - cell malignances (e.g.
or AML without cytogenetic changes. CLL), expression of only one light chain, κ or λ ,