Page 196 - Essential Haematology
P. 196
182 / Chapter 13 Acute myeloid leukaemia
(a)
(b)
(c)
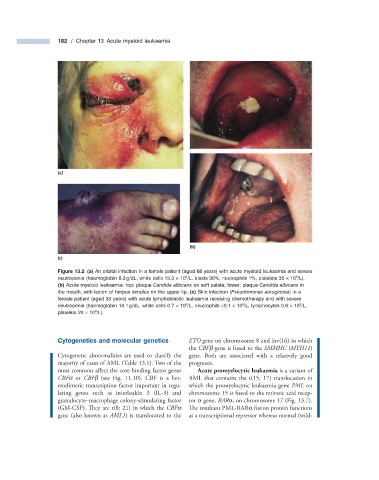
Figure 13.2 (a) An orbital infection in a female patient (aged 68 years) with acute myeloid leukaemia and severe
neutropenia (haemoglobin 8.3 g/dL, white cells 15.3 × 10 /L, blasts 96%, neutrophils 1%, platelets 30 × 10 /L).
9
9
(b) Acute myeloid leukaemia: top: plaque Candida albicans on soft palate; lower: plaque Candida albicans in
the mouth, with lesion of herpes simplex on the upper lip. (c) Skin infection ( Pseudomonas aeruginosa ) in a
female patient (aged 33 years) with acute lymphoblastic leukaemia receiving chemotherapy and with severe
9
9
neutropenia (haemoglobin 10.1 g/dL, white cells 0.7 × 10 /L, neutrophils < 0.1 × 10 /L, lymphocytes 0.6 × 10 /L,
9
platelets 20 × 10 /L).
9
Cytogenetics and m olecular g enetics ETO gene on chromosome 8 and inv(16) in which
the CBF β gene is fused to the SMMHC ( MYH11 )
Cytogenetic abnormalities are used to classify the gene. Both are associated with a relatively good
majority of cases of AML (Table 13.1 ). Two of the prognosis.
most common affect the core binding factor genes Acute promyelocytic leukaemia is a variant of
CBF α or CBF β (see Fig. 11.10 ). CBF is a het- AML that contains the t(15; 17) translocation in
erodimeric transcription factor important in regu- which the promyelocytic leukaemia gene PML on
lating genes such as interleukin 3 (IL - 3) and chromosome 15 is fused to the retinoic acid recep-
granulocyte – macrophage colony - stimulating factor tor α gene, RAR α , on chromosome 17 (Fig. 13.7 ).
(GM - CSF). They are t(8; 21) in which the CBF α The resultant PML - RAR α fusion protein functions
gene (also known as AML1 ) is translocated to the as a transcriptional repressor whereas normal (wild -