Page 330 - Essential Haematology
P. 330
316 / Chapter 24 Platelets, blood coagulation and haemostasis
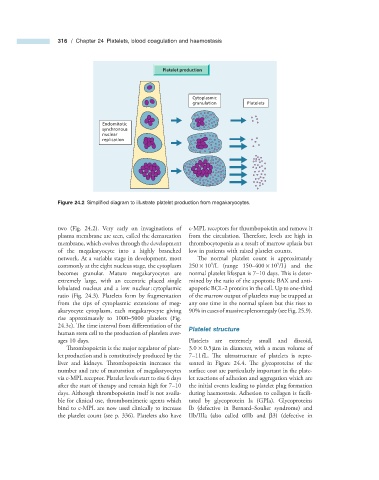
Platelet production
Cytoplasmic
granulation Platelets
Endomitotic
synchronous
nuclear
replication
Figure 24.2 Simplifi ed diagram to illustrate platelet production from megakaryocytes.
two (Fig. 24.2 ). Very early on invaginations of c - MPL receptors for thrombopoietin and remove it
plasma membrane are seen, called the demarcation from the circulation. Therefore, levels are high in
membrane, which evolves through the development thrombocytopenia as a result of marrow aplasia but
of the megakaryocyte into a highly branched low in patients with raised platelet counts.
network. At a variable stage in development, most The normal platelet count is approximately
9
9
commonly at the eight nucleus stage, the cytoplasm 250 × 10 /L (range 150 – 400 × 10 /L) and the
becomes granular. Mature megakaryocytes are normal platelet lifespan is 7 – 10 days. This is deter-
extremely large, with an eccentric placed single mined by the ratio of the apoptotic BAX and anti -
lobulated nucleus and a low nuclear : cytoplasmic apopotic BCL - 2 proteins in the cell. Up to one - third
ratio (Fig. 24.3 ). Platelets form by fragmentation of the marrow output of platelets may be trapped at
from the tips of cytoplasmic extensions of meg- any one time in the normal spleen but this rises to
akaryocyte cytoplasm, each megakaryocyte giving 90% in cases of massive splenomegaly (see Fig. 25.9 ) .
rise approximately to 1000 – 5000 platelets (Fig.
24.3 c). The time interval from differentiation of the Platelet s tructure
human stem cell to the production of platelets aver-
ages 10 days. Platelets are extremely small and discoid,
Thrombopoietin is the major regulator of plate- 3.0 × 0.5 μ m in diameter, with a mean volume of
let production and is constitutively produced by the 7 – 11 fL. The ultrastructure of platelets is repre-
liver and kidneys. Thrombopoietin increases the sented in Figure 24.4 . The glycoproteins of the
number and rate of maturation of megakaryocytes surface coat are particularly important in the plate-
via c - MPL receptor. Platelet levels start to rise 6 days let reactions of adhesion and aggregation which are
after the start of therapy and remain high for 7 – 10 the initial events leading to platelet plug formation
days. Although thrombopoietin itself is not availa- during haemostasis. Adhesion to collagen is facili-
ble for clinical use, thrombomimetic agents which tated by glycoprotein Ia (GPIa). Glycoproteins
bind to c - MPL are now used clinically to increase Ib (defective in Bernard – Soulier syndrome) and
the platelet count (see p. 336) . Platelets also have IIb/IIIa (also called α IIb and β 3) (defective in