Page 332 - Essential Haematology
P. 332
318 / Chapter 24 Platelets, blood coagulation and haemostasis
’
Glanzmann s thrombasthenia) are important in the release reaction described below, the contents of the
attachment of platelets to von Willebrand factor granules are discharged into the open canalicular
(VWF) and hence to vascular subendothelium system.
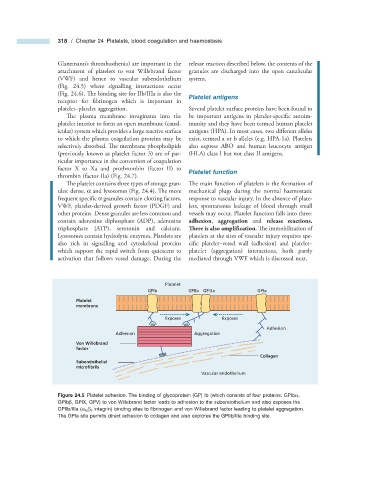
(Fig. 24.5 ) where signalling interactions occur
(Fig. 24.6 ). The binding site for IIb/IIIa is also the
Platelet a ntigens
receptor for fibrinogen which is important in
platelet – platelet aggregation. Several platelet surface proteins have been found to
The plasma membrane invaginates into the be important antigens in platelet - specifi c autoim-
platelet interior to form an open membrane (canal- munity and they have been termed human platelet
icular) system which provides a large reactive surface antigens (HPA). In most cases, two diff erent alleles
to which the plasma coagulation proteins may be exist, termed a or b alleles (e.g. HPA - 1a). Platelets
selectively absorbed. The membrane phospholipids also express ABO and human leucocyte antigen
(previously known as platelet factor 3) are of par- (HLA) class I but not class II antigens.
ticular importance in the conversion of coagulation
factor X to Xa and prothrombin (factor II) to
Platelet f unction
thrombin (factor IIa) (Fig. 24.7 ).
The platelet contains three types of storage gran- The main function of platelets is the formation of
ules: dense, α and lysosomes (Fig. 24.4 ). Th e more mechanical plugs during the normal haemostatic
frequent specifi c α granules contain clotting factors, response to vascular injury. In the absence of plate-
VWF, platelet - derived growth factor (PDGF) and lets, spontaneous leakage of blood through small
other proteins. Dense granules are less common and vessels may occur. Platelet function falls into three:
contain adenosine diphosphate (ADP), adenosine adhesion , aggregation and release reactions.
triphosphate (ATP), serotonin and calcium. There is also amplifi cation . The immobilization of
Lysosomes contain hydrolytic enzymes. Platelets are platelets at the sites of vascular injury requires spe-
also rich in signalling and cytoskeletal proteins cific platelet – vessel wall (adhesion) and platelet –
which support the rapid switch from quiescent to platelet (aggregation) interactions, both partly
activation that follows vessel damage. During the mediated through VWF which is discussed next.
Platelet
GPIb GPIIb GPIIIa GPIa
Platelet
membrane
Exposes Exposes
Adhesion
Adhesion Aggregation
Von Willebrand
factor
Collagen
Subendothelial
microfibrils
Vascular endothelium
Figure 24.5 Platelet adhesion. The binding of glycoprotein (GP) Ib (which consists of four proteins: GPIb α ,
GPIb β , GPIX, GPV) to von Willebrand factor leads to adhesion to the subendothelium and also exposes the
integrin) binding sites to fi brinogen and von Willebrand factor leading to platelet aggregation.
GPIIb/IIIa ( α IIb β 3
The GPIa site permits direct adhesion to collagen and also explores the GPIIb/IIIa binding site.