Page 333 - Essential Haematology
P. 333
Chapter 24 Platelets, blood coagulation and haemostasis / 319
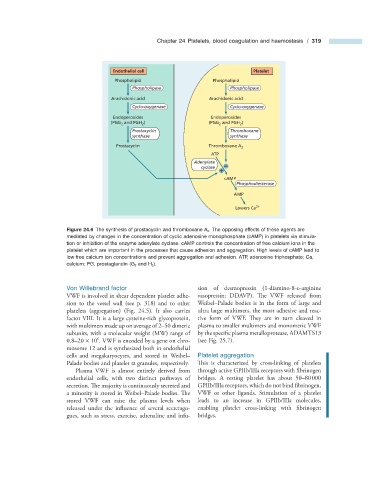
Endothelial cell Platelet
Phospholipid Phospholipid
Phospholipase Phospholipase
Arachidonic acid Arachidonic acid
Cyclo-oxygenase Cyclo-oxygenase
Endoperoxides Endoperoxides
(PGG and PGH ) (PGG and PGH )
2
2
2
2
Prostacyclin Thromboxane
synthase synthase
Prostacyclin Thromboxane A 2
ATP
Adenylate
cyclase
cAMP
Phosphodiesterase
AMP
Lowers Ca 2+
Figure 24.6 The synthesis of prostacyclin and thromboxane A 2 . The opposing effects of these agents are
mediated by changes in the concentration of cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) in platelets via stimula-
tion or inhibition of the enzyme adenylate cyclase. cAMP controls the concentration of free calcium ions in the
platelet which are important in the processes that cause adhesion and aggregation. High levels of cAMP lead to
low free calcium ion concentrations and prevent aggregation and adhesion. ATP, adenosine triphosphate; Ca,
calcium; PG, prostaglandin (G 2 and H 2 ).
Von Willebrand f actor sion of desmopressin (1 - diamino - 8 - D - arginine
VWF is involved in shear dependent platelet adhe- vasopressin; DDAVP). The VWF released from
sion to the vessel wall (see p. 318) and to other Weibel – Palade bodies is in the form of large and
platelets (aggregation) (Fig. 24.5 ). It also carries ultra large multimers, the most adhesive and reac-
factor VIII. It is a large cysteine - rich glycoprotein, tive form of VWF. They are in turn cleaved in
with multimers made up on average of 2 – 50 dimeric plasma to smaller multimers and monomeric VWF
subunits, with a molecular weight (MW) range of by the specific plasma metalloprotease, ADAMTS13
6
0.8 – 20 × 10 . VWF is encoded by a gene on chro- (see Fig. 25.7 ).
mosome 12 and is synthesized both in endothelial
cells and megakaryocytes, and stored in Weibel – Platelet a ggregation
Palade bodies and platelet α granules, respectively. This is characterized by cross - linking of platelets
Plasma VWF is almost entirely derived from through active GPIIb/IIIa receptors with fi brinogen
endothelial cells, with two distinct pathways of bridges. A resting platelet has about 50 – 80 000
secretion. The majority is continuously secreted and GPIIb/IIIa receptors, which do not bind fi brinogen,
a minority is stored in Weibel – Palade bodies. Th e VWF or other ligands. Stimulation of a platelet
stored VWF can raise the plasma levels when leads to an increase in GPIIb/IIIa molecules,
released under the influence of several secretago- enabling platelet cross - linking with fi brinogen
gues, such as stress, exercise, adrenaline and infu- bridges.