Page 353 - Essential Haematology
P. 353
Chapter 25 Bleeding disorders / 339
Plasma Endothelial cell
No platelet VWF multimers
aggregation
Protease cleaves
between tyrosine (842) VWF dimers
and methionine (843)
of monomeric substrate
VWF monomers
(a) NORMAL
VWF multimers
Platelet
aggregation
Ultra large
VWF multimers
Protease VWF dimers
Antibody
VWF monomers
(b) ACQUIRED TTP
VWF multimers
Platelet
aggregation
Ultra large
VWF multimers
VWF dimers
Protease absent
or defective
VWF monomers
(c) FAMILIAL TTP
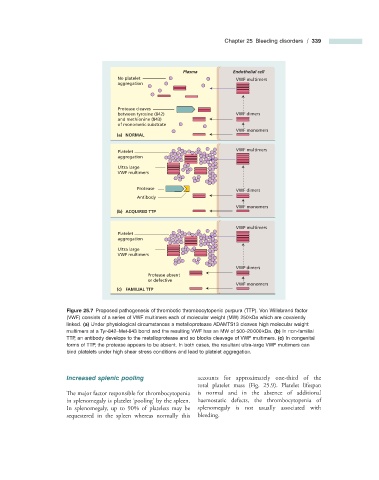
Figure 25.7 Proposed pathogenesis of thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura (TTP). Von Willebrand factor
(VWF) consists of a series of VWF multimers each of molecular weight (MW) 250 kDa which are covalently
linked. (a) Under physiological circumstances a metalloprotease ADAMTS13 cleaves high molecular weight
multimers at a Tyr - 842 – Met - 843 bond and the resulting VWF has an MW of 500 – 20 000 kDa. (b) In non - familial
TTP, an antibody develops to the metalloprotease and so blocks cleavage of VWF multimers. (c) In congenital
forms of TTP, the protease appears to be absent. In both cases, the resultant ultra - large VWF multimers can
bind platelets under high shear stress conditions and lead to platelet aggregation.
Increased s plenic p ooling accounts for approximately one - third of the
total platelet mass (Fig. 25.9 ). Platelet lifespan
The major factor responsible for thrombocytopenia is normal and in the absence of additional
in splenomegaly is platelet pooling ’ by the spleen. haemostatic defects, the thrombocytopenia of
‘
In splenomegaly, up to 90% of platelets may be splenomegaly is not usually associated with
sequestered in the spleen whereas normally this bleeding.