Page 352 - Essential Haematology
P. 352
338 / Chapter 25 Bleeding disorders
Antibody–drug–
Drug protein complex
Complement
Plasma
protein
B
cell
Antibody
C
Platelet
Platelet lysis
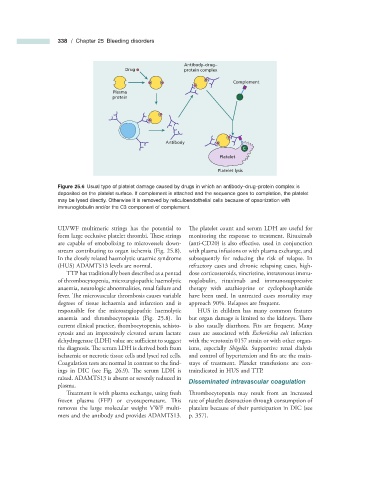
Figure 25.6 Usual type of platelet damage caused by drugs in which an antibody – drug – protein complex is
deposited on the platelet surface. If complement is attached and the sequence goes to completion, the platelet
may be lysed directly. Otherwise it is removed by reticuloendothelial cells because of opsonization with
immunoglobulin and/or the C3 component of complement.
ULVWF multimeric strings has the potential to The platelet count and serum LDH are useful for
form large occlusive platelet thrombi. Th ese strings monitoring the response to treatment. Rituximab
are capable of emobolizing to microvessels down- (anti - CD20) is also effective, used in conjunction
stream contributing to organ ischemia (Fig. 25.8 ). with plasma infusions or with plasma exchange, and
In the closely related haemolytic uraemic syndrome subsequently for reducing the risk of relapse. In
(HUS) ADAMTS13 levels are normal. refractory cases and chronic relapsing cases, high -
TTP has traditionally been described as a pentad dose corticosteroids, vincristine, intravenous immu-
of thrombocytopenia, microangiopathic haemolytic noglobulin, rituximab and immunosuppressive
anaemia, neurologic abnormalities, renal failure and therapy with azathioprine or cyclophosphamide
fever. The microvascular thrombosis causes variable have been used. In untreated cases mortality may
degrees of tissue ischaemia and infarction and is approach 90%. Relapses are frequent.
responsible for the microangiopathic haemolytic HUS in children has many common features
anaemia and thrombocytopenia (Fig. 25.8 ). In but organ damage is limited to the kidneys. Th ere
current clinical practice, thombocytopenia, schisto- is also usually diarrhoea. Fits are frequent. Many
cytosis and an impressively elevated serum lactate cases are associated with Escherichia coli infection
dehydrogenase (LDH) value are suffi cient to suggest with the verotoxin 0157 strain or with other organ-
the diagnosis. The serum LDH is derived both from isms, especially Shigella . Supportive renal dialysis
ischaemic or necrotic tissue cells and lysed red cells. and control of hypertension and fits are the main-
Coagulation tests are normal in contrast to the fi nd- stays of treatment. Platelet transfusions are con-
ings in DIC (see Fig. 26.9 ). The serum LDH is traindicated in HUS and TTP.
raised. ADAMTS13 is absent or severely reduced in Disseminated i ntravascular c oagulation
plasma.
Treatment is with plasma exchange, using fresh Thrombocytopenia may result from an increased
frozen plasma (FFP) or cryosupernatant. Th is rate of platelet destruction through consumption of
removes the large molecular weight VWF multi- platelets because of their participation in DIC (see
mers and the antibody and provides ADAMTS13. p. 357) .