Page 356 - Essential Haematology
P. 356
342 / Chapter 25 Bleeding disorders
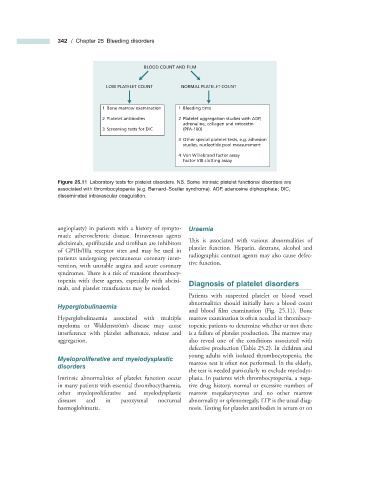
BLOOD COUNT AND FILM
LOW PLATELET COUNT NORMAL PLATELET COUNT
1 Bone marrow examination 1 Bleeding time
2 Platelet antibodies 2 Platelet aggregation studies with ADP,
adrenaline, collagen and ristocetin
3 Screening tests for DIC (PFA-100)
3 Other special platelet tests, e.g. adhesion
studies, nucleotide pool measurement
4 Von Willebrand factor assay
Factor VIII clotting assay
Figure 25.11 Laboratory tests for platelet disorders. NB. Some intrinsic platelet functional disorders are
associated with thrombocytopenia (e.g. Bernard – Soulier syndrome). ADP, adenosine diphosphate; DIC,
disseminated intravascular coagulation.
angioplasty) in patients with a history of sympto- Uraemia
matic atherosclerotic disease. Intravenous agents
This is associated with various abnormalities of
abciximab, eptifibatide and tirofiban are inhibitors
platelet function. Heparin, dextrans, alcohol and
of GPIIb/IIIa receptor sites and may be used in
radiographic contrast agents may also cause defec-
patients undergoing percutaneous coronary inter-
tive function.
vention, with unstable angina and acute coronary
syndromes. There is a risk of transient thrombocy-
topenia with these agents, especially with abcixi- Diagnosis of p latelet d isorders
mab, and platelet transfusions may be needed.
Patients with suspected platelet or blood vessel
abnormalities should initially have a blood count
Hyperglobulinaemia
and blood film examination (Fig. 25.11 ). Bone
Hyperglobulinaemia associated with multiple marrow examination is often needed in thrombocy-
myeloma or Waldenstr ö m ’ s disease may cause topenic patients to determine whether or not there
interference with platelet adherence, release and is a failure of platelet production. The marrow may
aggregation. also reveal one of the conditions associated with
defective production (Table 25.2 ). In children and
young adults with isolated thrombocytopenia, the
Myeloproliferative and m yelodysplastic
d isorders marrow test is often not performed. In the elderly,
the test is needed particularly to exclude myelodys-
Intrinsic abnormalities of platelet function occur plasia. In patients with thrombocytopenia, a nega-
in many patients with essential thrombocythaemia, tive drug history, normal or excessive numbers of
other myeloproliferative and myelodysplastic marrow megakaryocytes and no other marrow
diseases and in paroxysmal nocturnal abnormality or splenomegaly, ITP is the usual diag-
haemoglobinuria. nosis. Testing for platelet antibodies in serum or on