Page 379 - Essential Haematology
P. 379
Chapter 27 Thrombosis and antithrombotic therapy / 365
(a) (b)
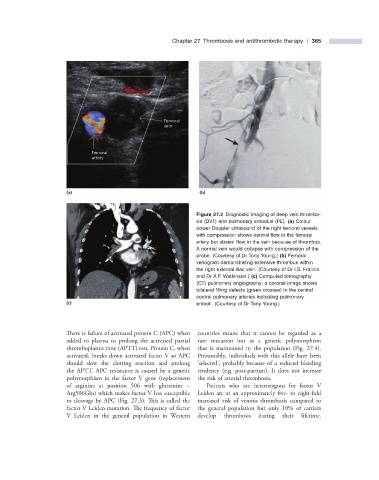
Figure 27.2 Diagnostic imaging of deep vein thrombo-
sis (DVT) and pulmonary embolus (PE). (a) Colour
power Doppler ultrasound of the right femoral vessels
with compression shows normal fl ow in the femoral
artery but absent fl ow in the vein because of thrombus.
A normal vein would collapse with compression of the
probe. (Courtesy of Dr Tony Young.) (b) Femoral
venogram demonstrating extensive thrombus within
the right external iliac vein. (Courtesy of Dr I.S. Francis
and Dr A.F. Watkinson.) (c) Computed tomography
(CT) pulmonary angiography: a coronal image shows
bilateral fi lling defects (green crosses) in the central
central pulmonary arteries indicating pulmonary
(c) emboli. (Courtesy of Dr Tony Young.)
There is failure of activated protein C (APC) when countries means that it cannot be regarded as a
added to plasma to prolong the activated partial rare mutation but as a genetic polymorphism
thromboplastin time (APTT) test. Protein C, when that is maintained in the population (Fig. 27.4 ).
activated, breaks down activated factor V so APC Presumably, individuals with this allele have been
‘
should slow the clotting reaction and prolong selected ’ , probably because of a reduced bleeding
the APTT. APC resistance is caused by a genetic tendency (e.g. post - partum). It does not increase
polymorphism in the factor V gene (replacement the risk of arterial thrombosis.
of arginine at position 506 with glutamine – Patients who are heterozygous for factor V
Arg506Gln) which makes factor V less susceptible Leiden are at an approximately five - to eight - fold
to cleavage by APC (Fig. 27.3 ). This is called the increased risk of venous thrombosis compared to
factor V Leiden mutation. The frequency of factor the general population but only 10% of carriers
V Leiden in the general population in Western develop thrombosis during their lifetime.