Page 382 - Essential Haematology
P. 382
368 / Chapter 27 Thrombosis and antithrombotic therapy
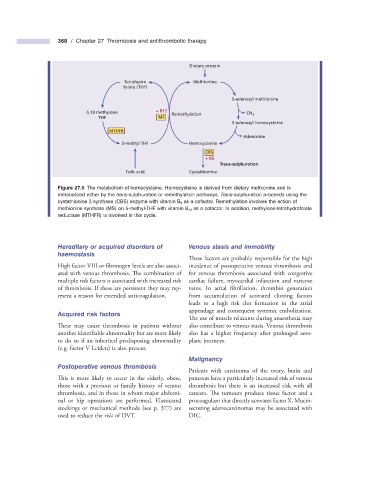
Dietary protein
Tetrahydro Methionine
folate (THF)
S-adenosyl methionine
5,10 methylene + B12 Remethylation CH 3
THF MS
S-adenosyl homocysteine
MTHFR
Adenosine
S-methyl THF Homocysteine
CBS
+ B6
Trans-sulphuration
Folic acid Cystathionine
Figure 27.5 The metabolism of homocysteine. Homocysteine is derived from dietary methionine and is
metabolized either by the trans - sulphuration or remethylation pathways. Trans - sulphuration proceeds using the
cystathionine β - synthase (CBS) enzyme with vitamin B 6 as a cofactor. Remethylation involves the action of
methionine synthase (MS) on 5 - methyl - THF with vitamin B 12 as a cofactor. In addition, methylene - tetrahydrofolate
reductase (MTHFR) is involved in this cycle.
Hereditary or a cquired d isorders of Venous s tasis and i mmobility
h aemostasis
These factors are probably responsible for the high
High factor VIII or fibrinogen levels are also associ- incidence of postoperative venous thrombosis and
ated with venous thrombosis. The combination of for venous thrombosis associated with congestive
multiple risk factors is associated with increased risk cardiac failure, myocardial infarction and varicose
of thrombosis. If these are persistent they may rep- veins. In atrial fibrillation, thrombin generation
resent a reason for extended anticoagulation. from accumulation of activated clotting factors
leads to a high risk clot formation in the atrial
appendage and consequent systemic embolization.
Acquired r isk f actors
The use of muscle relaxants during anaesthesia may
These may cause thrombosis in patients without also contribute to venous stasis. Venous thrombosis
another identifiable abnormality but are more likely also has a higher frequency after prolonged aero-
to do so if an inherited predisposing abnormality plane journeys.
(e.g. factor V Leiden) is also present.
Malignancy
Postoperative v enous t hrombosis
Patients with carcinoma of the ovary, brain and
This is more likely to occur in the elderly, obese, pancreas have a particularly increased risk of venous
those with a previous or family history of venous thrombosis but there is an increased risk with all
thrombosis, and in those in whom major abdomi- cancers. The tumours produce tissue factor and a
nal or hip operations are performed. Elasticated procoagulant that directly activates factor X. Mucin -
stockings or mechanical methods (see p. 377) are secreting adenocarcinomas may be associated with
used to reduce the risk of DVT. DIC.