Page 380 - Essential Haematology
P. 380
366 / Chapter 27 Thrombosis and antithrombotic therapy
Individuals who are homozygous have a 30 – 140 -
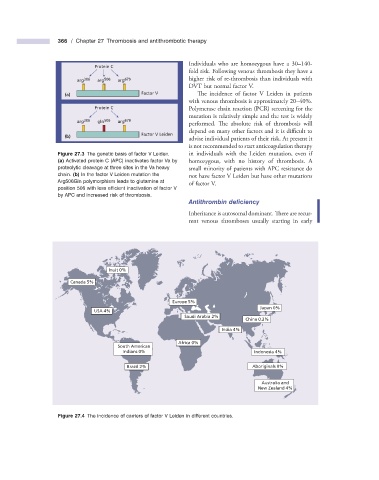
Protein C
fold risk. Following venous thrombosis they have a
arg 306 arg 506 arg 679 higher risk of re - thrombosis than individuals with
DVT but normal factor V.
(a) Factor V The incidence of factor V Leiden in patients
with venous thrombosis is approximately 20 – 40%.
Protein C Polymerase chain reaction (PCR) screening for the
mutation is relatively simple and the test is widely
arg 306 gln 506 arg 679
performed. The absolute risk of thrombosis will
depend on many other factors and it is diffi cult to
Factor V Leiden
(b)
advise individual patients of their risk. At present it
is not recommended to start anticoagulation therapy
Figure 27.3 The genetic basis of factor V Leiden. in individuals with the Leiden mutation, even if
(a) Activated protein C (APC) inactivates factor Va by homozygous, with no history of thrombosis. A
proteolytic cleavage at three sites in the Va heavy small minority of patients with APC resistance do
chain. (b) In the factor V Leiden mutation the not have factor V Leiden but have other mutations
Arg506Gln polymorphism leads to glutamine at
of factor V.
position 506 with less effi cient inactivation of factor V
by APC and increased risk of thrombosis.
Antithrombin d efi ciency
Inheritance is autosomal dominant. There are recur-
rent venous thromboses usually starting in early
Inuit 0%
Canada 5%
Europe 5%
Japan 0%
USA 4%
Saudi Arabia 2%
China 0.2%
India 4%
Africa 0%
South American
Indians 0% Indonesia 4%
Brazil 2% Aboriginals 0%
Australia and
New Zealand 4%
Figure 27.4 The incidence of carriers of factor V Leiden in different countries.