Page 229 - parasitology for medical and clinical laboratoryprofessionals
P. 229
Invasive Tissue Parasites 209
CT scans (computerized tomography), and in some
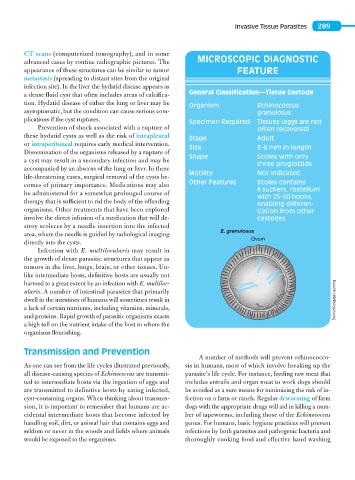
advanced cases by routine radiographic pictures. The MICROSCOPIC DIAGNOSTIC
appearance of these structures can be similar to tumor FEATURE
metastasis (spreading to distant sites from the original
infection site). In the liver the hydatid disease appears as
a dense fluid cyst that often includes areas of calcifica- General Classification—Tissue Cestode
tion. Hydatid disease of either the lung or liver may be Organism Echinococcus
asymptomatic, but the condition can cause serious com- granulosus
plications if the cyst ruptures. Specimen Required Tissues (eggs are not
Prevention of shock associated with a rupture of often recovered)
these hydatid cysts as well as the risk of intrapleural Stage Adult
or intraperitoneal requires early medical intervention. Size 3–6 mm in length
Dissemination of the organisms released by a rupture of
a cyst may result in a secondary infection and may be Shape Scolex with only
three proglottids
accompanied by an abscess of the lung or liver. In these
life-threatening cases, surgical removal of the cysts be- Motility Not indicated
comes of primary importance. Medications may also Other Features Scolex contains
be administered for a somewhat prolonged course of 4 suckers, rostellum
with 25–50 hooks,
therapy that is sufficient to rid the body of the offending enabling differen-
organisms. Other treatments that have been explored tiation from other
involve the direct infusion of a medication that will de- cestodes
stroy scoleces by a needle insertion into the infected
E. granulosus
area, where the needle is guided by radiological imaging
Ovum
directly into the cysts.
Infection with E. multilocularis may result in
the growth of dense parasitic structures that appear as
tumors in the liver, lungs, brain, or other tissues. Un-
like intermediate hosts, definitive hosts are usually not
harmed to a great extent by an infection with E. multiloc-
ularis. A number of intestinal parasites that primarily
dwell in the intestines of humans will sometimes result in Delmar/Cengage Learning
a lack of certain nutrients, including vitamins, minerals,
and proteins. Rapid growth of parasitic organisms exacts
a high toll on the nutrient intake of the host in whom the
organisms flourishing.
Transmission and Prevention
A number of methods will prevent echinococco-
As one can see from the life cycles illustrated previously, sis in humans, most of which involve breaking up the
all disease-causing species of Echinococcus are transmit- parasite’s life cycle. For instance, feeding raw meat that
ted to intermediate hosts via the ingestion of eggs and includes entrails and organ meat to work dogs should
are transmitted to definitive hosts by eating infected, be avoided as a sure means for minimizing the risk of in-
cyst-containing organs. When thinking about transmis- fection on a farm or ranch. Regular deworming of farm
sion, it is important to remember that humans are ac- dogs with the appropriate drugs will aid in killing a num-
cidental intermediate hosts that become infected by ber of tapeworms, including those of the Echinococcus
handling soil, dirt, or animal hair that contains eggs and genus. For humans, basic hygiene practices will prevent
seldom or never in the woods and fields where animals infections by both parasites and pathogenic bacteria and
would be exposed to the organisms. thoroughly cooking food and effective hand washing