Page 456 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 456
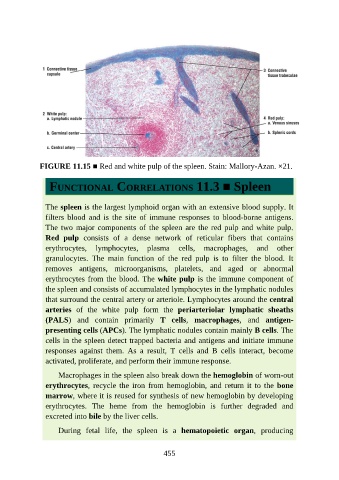
FIGURE 11.15 ■ Red and white pulp of the spleen. Stain: Mallory-Azan. ×21.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 11.3 ■ Spleen
The spleen is the largest lymphoid organ with an extensive blood supply. It
filters blood and is the site of immune responses to blood-borne antigens.
The two major components of the spleen are the red pulp and white pulp.
Red pulp consists of a dense network of reticular fibers that contains
erythrocytes, lymphocytes, plasma cells, macrophages, and other
granulocytes. The main function of the red pulp is to filter the blood. It
removes antigens, microorganisms, platelets, and aged or abnormal
erythrocytes from the blood. The white pulp is the immune component of
the spleen and consists of accumulated lymphocytes in the lymphatic nodules
that surround the central artery or arteriole. Lymphocytes around the central
arteries of the white pulp form the periarteriolar lymphatic sheaths
(PALS) and contain primarily T cells, macrophages, and antigen-
presenting cells (APCs). The lymphatic nodules contain mainly B cells. The
cells in the spleen detect trapped bacteria and antigens and initiate immune
responses against them. As a result, T cells and B cells interact, become
activated, proliferate, and perform their immune response.
Macrophages in the spleen also break down the hemoglobin of worn-out
erythrocytes, recycle the iron from hemoglobin, and return it to the bone
marrow, where it is reused for synthesis of new hemoglobin by developing
erythrocytes. The heme from the hemoglobin is further degraded and
excreted into bile by the liver cells.
During fetal life, the spleen is a hematopoietic organ, producing
455