Page 523 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 523
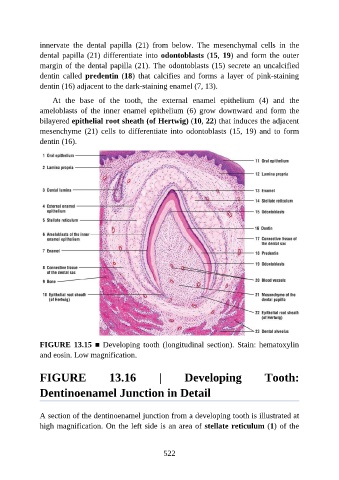
innervate the dental papilla (21) from below. The mesenchymal cells in the
dental papilla (21) differentiate into odontoblasts (15, 19) and form the outer
margin of the dental papilla (21). The odontoblasts (15) secrete an uncalcified
dentin called predentin (18) that calcifies and forms a layer of pink-staining
dentin (16) adjacent to the dark-staining enamel (7, 13).
At the base of the tooth, the external enamel epithelium (4) and the
ameloblasts of the inner enamel epithelium (6) grow downward and form the
bilayered epithelial root sheath (of Hertwig) (10, 22) that induces the adjacent
mesenchyme (21) cells to differentiate into odontoblasts (15, 19) and to form
dentin (16).
FIGURE 13.15 ■ Developing tooth (longitudinal section). Stain: hematoxylin
and eosin. Low magnification.
FIGURE 13.16 | Developing Tooth:
Dentinoenamel Junction in Detail
A section of the dentinoenamel junction from a developing tooth is illustrated at
high magnification. On the left side is an area of stellate reticulum (1) of the
522