Page 524 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 524
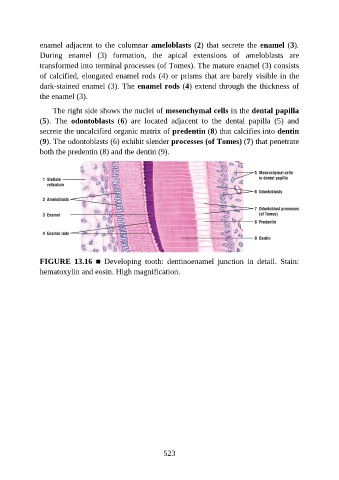
enamel adjacent to the columnar ameloblasts (2) that secrete the enamel (3).
During enamel (3) formation, the apical extensions of ameloblasts are
transformed into terminal processes (of Tomes). The mature enamel (3) consists
of calcified, elongated enamel rods (4) or prisms that are barely visible in the
dark-stained enamel (3). The enamel rods (4) extend through the thickness of
the enamel (3).
The right side shows the nuclei of mesenchymal cells in the dental papilla
(5). The odontoblasts (6) are located adjacent to the dental papilla (5) and
secrete the uncalcified organic matrix of predentin (8) that calcifies into dentin
(9). The odontoblasts (6) exhibit slender processes (of Tomes) (7) that penetrate
both the predentin (8) and the dentin (9).
FIGURE 13.16 ■ Developing tooth: dentinoenamel junction in detail. Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. High magnification.
523