Page 521 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 521
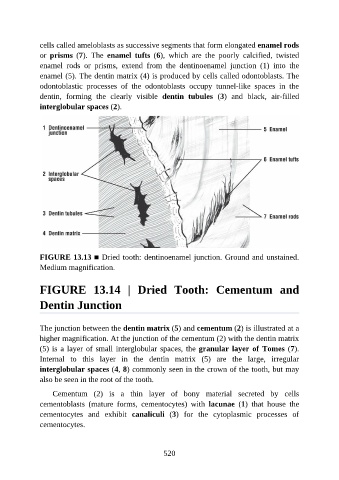
cells called ameloblasts as successive segments that form elongated enamel rods
or prisms (7). The enamel tufts (6), which are the poorly calcified, twisted
enamel rods or prisms, extend from the dentinoenamel junction (1) into the
enamel (5). The dentin matrix (4) is produced by cells called odontoblasts. The
odontoblastic processes of the odontoblasts occupy tunnel-like spaces in the
dentin, forming the clearly visible dentin tubules (3) and black, air-filled
interglobular spaces (2).
FIGURE 13.13 ■ Dried tooth: dentinoenamel junction. Ground and unstained.
Medium magnification.
FIGURE 13.14 | Dried Tooth: Cementum and
Dentin Junction
The junction between the dentin matrix (5) and cementum (2) is illustrated at a
higher magnification. At the junction of the cementum (2) with the dentin matrix
(5) is a layer of small interglobular spaces, the granular layer of Tomes (7).
Internal to this layer in the dentin matrix (5) are the large, irregular
interglobular spaces (4, 8) commonly seen in the crown of the tooth, but may
also be seen in the root of the tooth.
Cementum (2) is a thin layer of bony material secreted by cells
cementoblasts (mature forms, cementocytes) with lacunae (1) that house the
cementocytes and exhibit canaliculi (3) for the cytoplasmic processes of
cementocytes.
520