Page 592 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 592
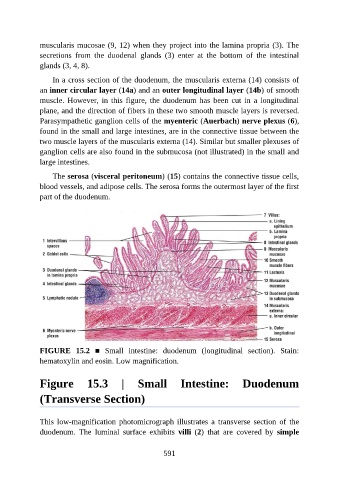
muscularis mucosae (9, 12) when they project into the lamina propria (3). The
secretions from the duodenal glands (3) enter at the bottom of the intestinal
glands (3, 4, 8).
In a cross section of the duodenum, the muscularis externa (14) consists of
an inner circular layer (14a) and an outer longitudinal layer (14b) of smooth
muscle. However, in this figure, the duodenum has been cut in a longitudinal
plane, and the direction of fibers in these two smooth muscle layers is reversed.
Parasympathetic ganglion cells of the myenteric (Auerbach) nerve plexus (6),
found in the small and large intestines, are in the connective tissue between the
two muscle layers of the muscularis externa (14). Similar but smaller plexuses of
ganglion cells are also found in the submucosa (not illustrated) in the small and
large intestines.
The serosa (visceral peritoneum) (15) contains the connective tissue cells,
blood vessels, and adipose cells. The serosa forms the outermost layer of the first
part of the duodenum.
FIGURE 15.2 ■ Small intestine: duodenum (longitudinal section). Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. Low magnification.
Figure 15.3 | Small Intestine: Duodenum
(Transverse Section)
This low-magnification photomicrograph illustrates a transverse section of the
duodenum. The luminal surface exhibits villi (2) that are covered by simple
591