Page 596 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 596
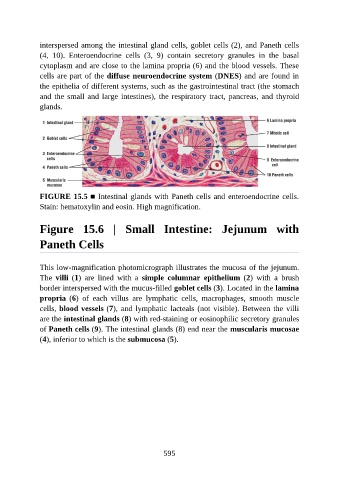
interspersed among the intestinal gland cells, goblet cells (2), and Paneth cells
(4, 10). Enteroendocrine cells (3, 9) contain secretory granules in the basal
cytoplasm and are close to the lamina propria (6) and the blood vessels. These
cells are part of the diffuse neuroendocrine system (DNES) and are found in
the epithelia of different systems, such as the gastrointestinal tract (the stomach
and the small and large intestines), the respiratory tract, pancreas, and thyroid
glands.
FIGURE 15.5 ■ Intestinal glands with Paneth cells and enteroendocrine cells.
Stain: hematoxylin and eosin. High magnification.
Figure 15.6 | Small Intestine: Jejunum with
Paneth Cells
This low-magnification photomicrograph illustrates the mucosa of the jejunum.
The villi (1) are lined with a simple columnar epithelium (2) with a brush
border interspersed with the mucus-filled goblet cells (3). Located in the lamina
propria (6) of each villus are lymphatic cells, macrophages, smooth muscle
cells, blood vessels (7), and lymphatic lacteals (not visible). Between the villi
are the intestinal glands (8) with red-staining or eosinophilic secretory granules
of Paneth cells (9). The intestinal glands (8) end near the muscularis mucosae
(4), inferior to which is the submucosa (5).
595