Page 593 - Atlas of Histology with Functional Correlations
P. 593
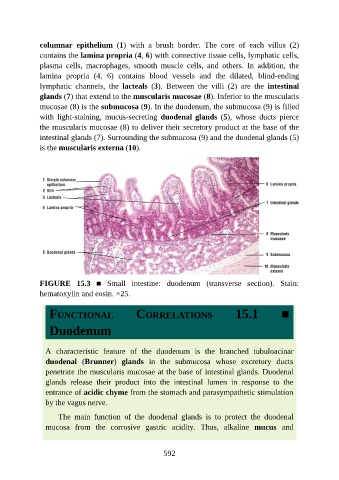
columnar epithelium (1) with a brush border. The core of each villus (2)
contains the lamina propria (4, 6) with connective tissue cells, lymphatic cells,
plasma cells, macrophages, smooth muscle cells, and others. In addition, the
lamina propria (4, 6) contains blood vessels and the dilated, blind-ending
lymphatic channels, the lacteals (3). Between the villi (2) are the intestinal
glands (7) that extend to the muscularis mucosae (8). Inferior to the muscularis
mucosae (8) is the submucosa (9). In the duodenum, the submucosa (9) is filled
with light-staining, mucus-secreting duodenal glands (5), whose ducts pierce
the muscularis mucosae (8) to deliver their secretory product at the base of the
intestinal glands (7). Surrounding the submucosa (9) and the duodenal glands (5)
is the muscularis externa (10).
FIGURE 15.3 ■ Small intestine: duodenum (transverse section). Stain:
hematoxylin and eosin. ×25.
FUNCTIONAL CORRELATIONS 15.1 ■
Duodenum
A characteristic feature of the duodenum is the branched tubuloacinar
duodenal (Brunner) glands in the submucosa whose excretory ducts
penetrate the muscularis mucosae at the base of intestinal glands. Duodenal
glands release their product into the intestinal lumen in response to the
entrance of acidic chyme from the stomach and parasympathetic stimulation
by the vagus nerve.
The main function of the duodenal glands is to protect the duodenal
mucosa from the corrosive gastric acidity. Thus, alkaline mucus and
592