Page 589 - Wago_PCB_TerminalBlocksConnectors_Volume2_2015_US
P. 589
13
587
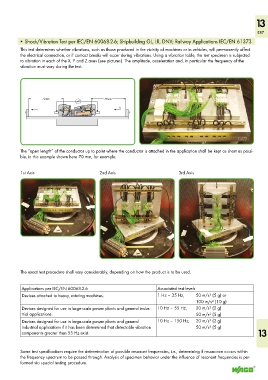
• Shock/Vibration Test per IEC/EN 60068-2-6; Shipbuilding GL, LR, DNV; Railway Applications IEC/EN 61373
This test determines whether vibrations, such as those produced in the vicinity of machines or in vehicles, will permanently affect
the electrical connection, or if contact breaks will occur during vibrations. Using a vibration table, the test specimen is subjected
to vibration in each of the X, Y and Z axes (see pictures). The amplitude, acceleration and, in particular the frequency of the
vibration must vary during the test.
<_________ 70 mm ________> <_________ 70 mm ________>
mV
I t
The “open length” of the conductor up to point where the conductor is attached in the application shall be kept as short as possi-
ble, in this example shown here 70 mm, for example.
1st Axis 2nd Axis 3rd Axis
The exact test procedure shall vary considerably, depending on how the product is to be used.
Applications per IEC/EN 60068-2-6 Associated test levels
Devices attached to heavy, rotating machines. 1 Hz – 35 Hz, 50 m/s² (5 g) or
100 m/s² (10 g)
Devices designed for use in large-scale power plants and general indus- 10 Hz – 55 Hz, 20 m/s² (2 g)
trial applications. 50 m/s² (5 g)
Devices designed for use in large-scale power plants and general 10 Hz – 150 Hz, 20 m/s² (2 g)
industrial applications if it has been determined that detectable vibration 50 m/s² (5 g)
components greater than 55 Hz exist. 13
Some test specifications require the determination of possible resonant frequencies, i.e., determining if resonance occurs within
the frequency spectrum to be passed through. Analysis of specimen behavior under the influence of resonant frequencies is per-
formed via special testing procedure.