Page 438 - Mechatronics with Experiments
P. 438
JWST499-Cetinkunt
JWST499-c07
424 MECHATRONICS Printer: Yet to Come October 9, 2014 8:41 254mm×178mm
of pump displacement is performed by the control valve which is actuated based on the
control objective. In closed circuit hydraulic circuits, ideally there is no leakage nor need
for replenishment fluid. In reality, it is desirable to have a certain amount of leakage. It is
through the leakage and the replenishment circuits that fluid under high pressure is removed
from the main loop, cooled by the heat exhanger, cleaned by filters and reinjected back
into the main loop. Therefore, the leakage and charge pump relenishment is an essential
part of all practical closed circuit hydraulic systems. In fact, the leakage rate is planned
into the circuit design and regulated at a planned rate by a so called loop flushing valve.
A typical system also includes various pressure relief valves between different sides of
hydraulic lines.
The pump is a variable displacement type bidirectional pump. By changing the direc-
tion of fluid flow, the direction of speed of the hydraulic motor is changed. By controlling
the pump, the flow rate and hence the speed of the hydraulic motor, is controlled. Similarly,
if the pump is controlled to maintain a certain pressure, the torque output at the hydraulic
motor is controlled.
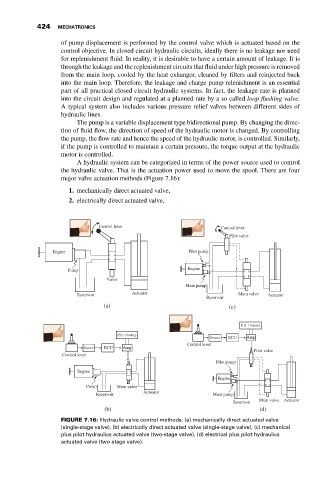
A hydraulic system can be categorized in terms of the power source used to control
the hydraulic valve. That is the actuation power used to move the spool. There are four
major valve actuation methods (Figure 7.16):
1. mechanically direct actuated valve,
2. electrically direct actuated valve,
Control lever Control lever
Pilot valve
Engine Pilot pump
Engine
Pump
Valve
Main pump
Actuator Main valve
Reservoir Actuator
Reservoir
(a) (c)
P.S. / battery
P.S. / battery
Sensor ECU Amp
Control lever
Sensor ECU Amp
Pilot valve
Control lever
Pilot pump
Engine
Engine
Pump Main valve
Actuator
Reservoir Main pump
Main valve Actuator
Reservoir
(b) (d)
FIGURE 7.16: Hydraulic valve control methods: (a) mechanically direct actuated valve
(single-stage valve), (b) electrically direct actuated valve (single-stage valve), (c) mechanical
plus pilot hydraulics actuated valve (two-stage valve), (d) electrical plus pilot hydraulics
actuated valve (two-stage valve).