Page 131 - Servo Motors and Industrial Control Theory -
P. 131
126 7 Electrohydraulic Servo Motors
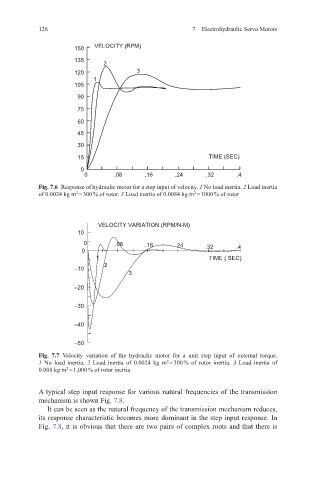
150 VELOCITY (RPM)
135
2
120 3
1
105
90
75
60
45
30
15 TIME (SEC)
0
0 .08 .16 .24 .32 .4
Fig. 7.6 Response of hydraulic motor for a step input of velocity. 1 No load inertia. 2 Load inertia
2
of 0.0024 kg m = 300 % of rotor. 3 Load inertia of 0.0084 kg m = 1000 % of rotor
2
VELOCITY VARIATION (RPM/N-M)
10
0 .08 .16 24 .32
0 .4
1 TIME ( SEC)
2
–10
3
–20
–30
–40
–50
Fig. 7.7 Velocity variation of the hydraulic motor for a unit step input of external torque.
1 No load inertia. 2 Load inertia of 0.0024 kg m = 300 % of rotor inertia. 3 Load inertia of
2
0.008 kg m = 1,000 % of rotor inertia
2
A typical step input response for various natural frequencies of the transmission
mechanism is shown Fig. 7.8.
It can be seen as the natural frequency of the transmission mechanism reduces,
its response characteristic becomes more dominant in the step input response. In
Fig. 7.8, it is obvious that there are two pairs of complex roots and that there is