Page 449 - Most-Essential-Learning-Competencies-Matrix-LATEST-EDITION-FROM-BCD
P. 449
449
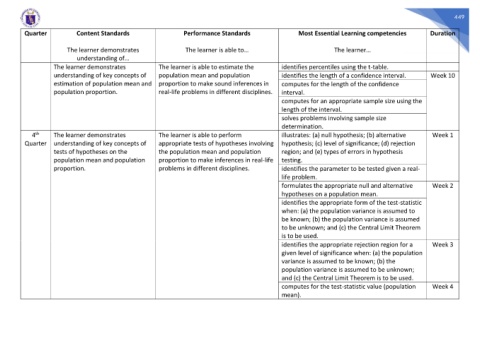
Quarter Content Standards Performance Standards Most Essential Learning competencies Duration
The learner demonstrates The learner is able to… The learner…
understanding of…
The learner demonstrates The learner is able to estimate the identifies percentiles using the t-table.
understanding of key concepts of population mean and population identifies the length of a confidence interval. Week 10
estimation of population mean and proportion to make sound inferences in computes for the length of the confidence
population proportion. real-life problems in different disciplines. interval.
computes for an appropriate sample size using the
length of the interval.
solves problems involving sample size
determination.
th
4 The learner demonstrates The learner is able to perform illustrates: (a) null hypothesis; (b) alternative Week 1
Quarter understanding of key concepts of appropriate tests of hypotheses involving hypothesis; (c) level of significance; (d) rejection
tests of hypotheses on the the population mean and population region; and (e) types of errors in hypothesis
population mean and population proportion to make inferences in real-life testing.
proportion. problems in different disciplines. identifies the parameter to be tested given a real-
life problem.
formulates the appropriate null and alternative Week 2
hypotheses on a population mean.
identifies the appropriate form of the test-statistic
when: (a) the population variance is assumed to
be known; (b) the population variance is assumed
to be unknown; and (c) the Central Limit Theorem
is to be used.
identifies the appropriate rejection region for a Week 3
given level of significance when: (a) the population
variance is assumed to be known; (b) the
population variance is assumed to be unknown;
and (c) the Central Limit Theorem is to be used.
computes for the test-statistic value (population Week 4
mean).