Page 14 - january
P. 14
PRODUCTION AUTOMATION
The control signal is generated by a PID (proportional-integral-differential) controller in
the USO in the range from 0 to 200% of the nominal value of the adaptation parameter. Thus, a
2-fold increase in productivity can be achieved. At the same time, the adaptation of the machining
mode allows the tool to be used in a partial execution mode. In addition, the introduction of the
VA channel makes it possible to implement control algorithms aimed at stabilizing the cutting
process in the event of intense self-oscillations, which deteriorate the surface quality and can
provoke a breakdown of the RI. Another feature of self-oscillations is the fact that when they
occur, the cutting forces and, accordingly, the power consumption are usually reduced. If in this
situation we rely only on information about the current power value, then the picture will look
as if, for example, the depth of cut has decreased. In fig. 2 shows an example of the spectra
of VA signals accompanying the turning of a steel billet in the same modes, but with different
dynamic stiffness of the technological system. Figure 2a shows the spectrum of the VA signal
accompanying processing with the usual overhang of the cutter and the tailstock quill, and
Figure 2b - signal spectrum at increased overhangs. In the second case, the power consumption
was less by 25%, although the values of the spectral maxima have grown tenfold. The presence
of only the power control channel does not allow the DS to correctly identify this situation and
make the necessary decision to correct it.
Control signal
CS (to the CNC PLC)
VS
USO
UZ FNCh FVCh
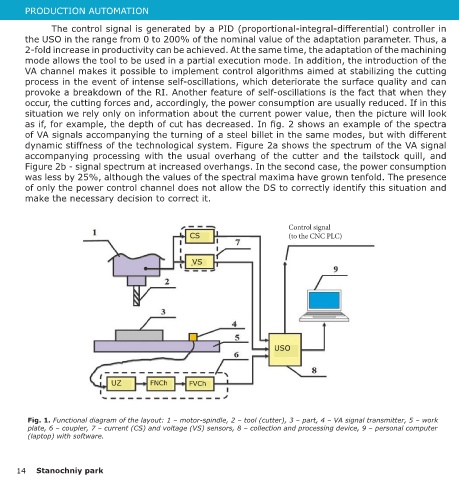
Fig. 1. Functional diagram of the layout: 1 ‒ motor-spindle, 2 ‒ tool (cutter), 3 ‒ part, 4 ‒ VA signal transmitter, 5 ‒ work
plate, 6 ‒ coupler, 7 ‒ current (CS) and voltage (VS) sensors, 8 ‒ collection and processing device, 9 ‒ personal computer
(laptop) with software.
14 Stanochniy park