Page 75 - The Truth Landscape Format 2020 with next section introductions-compressed
P. 75
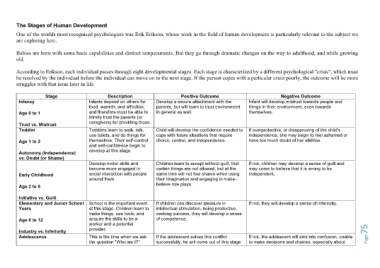
The Stages of Human Development
One of the worlds most recognised psychologists was Erik Erikson, whose work in the field of human development is particularly relevant to the subject we
are exploring here.
Babies are born with some basic capabilities and distinct temperaments. But they go through dramatic changes on the way to adulthood, and while growing
old.
According to Erikson, each individual passes through eight developmental stages. Each stage is characterized by a different psychological "crisis", which must
be resolved by the individual before the individual can move on to the next stage. If the person copes with a particular crisis poorly, the outcome will be more
struggles with that issue later in life.
Stage Description Positive Outcome Negative Outcome
Infancy Infants depend on others for Develop a secure attachment with the Infant will develop mistrust towards people and
food, warmth, and affection, parents, but will learn to trust environment things in their environment, even towards
Age 0 to 1 and therefore must be able to in general as well. themselves.
blindly trust the parents (or
Trust vs. Mistrust caregivers) for providing those.
Toddler Toddlers learn to walk, talk, Child will develop the confidence needed to If overprotective, or disapproving of the child's
use toilets, and do things for cope with future situations that require independence, she may begin to feel ashamed or
Age 1 to 2 themselves. Their self-control choice, control, and independence. have too much doubt of her abilities.
and self-confidence begin to
Autonomy (Independence) develop at this stage.
vs. Doubt (or Shame)
Develop motor skills and Children learn to accept without guilt, that If not, children may develop a sense of guilt and
become more engaged in certain things are not allowed, but at the may come to believe that it is wrong to be
Early Childhood social interaction with people same time will not feel shame when using independent.
around them. their imagination and engaging in make-
Age 2 to 6 believe role plays.
Initiative vs. Guilt
Elementary and Junior School School is the important event If children can discover pleasure in If not, they will develop a sense of inferiority.
Years at this stage. Children learn to intellectual stimulation, being productive,
make things, use tools, and seeking success, they will develop a sense
Age 6 to 12 acquire the skills to be a of competence.
worker and a potential
Industry vs. Inferiority provider. Page75
Adolescence This is the time when we ask If the adolescent solves this conflict If not, the adolescent will sink into confusion, unable
the question "Who am I?" successfully, he will come out of this stage to make decisions and choices, especially about