Page 36 - June
P. 36
METALWORKING EQUIPMENT AND TOOLS
that there are vibration modes that, when released from the bonds, at the first moment move
from the cutting surface (Fig. 4). These are high-frequency forms that manage to manifest
themselves in the initial moments after the disappearance of connections, outstripping the
movement of low-frequency forms in the opposite direction. But then the direction of movement
changes towards the cutting surface, contributing to the impact interaction of the tool and the
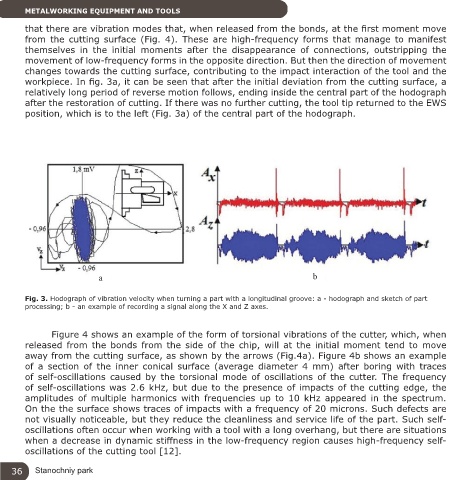
workpiece. In fig. 3a, it can be seen that after the initial deviation from the cutting surface, a
relatively long period of reverse motion follows, ending inside the central part of the hodograph
after the restoration of cutting. If there was no further cutting, the tool tip returned to the EWS
position, which is to the left (Fig. 3a) of the central part of the hodograph.
a b
Fig. 3. Hodograph of vibration velocity when turning a part with a longitudinal groove: a - hodograph and sketch of part
processing; b - an example of recording a signal along the X and Z axes.
Figure 4 shows an example of the form of torsional vibrations of the cutter, which, when
released from the bonds from the side of the chip, will at the initial moment tend to move
away from the cutting surface, as shown by the arrows (Fig.4a). Figure 4b shows an example
of a section of the inner conical surface (average diameter 4 mm) after boring with traces
of self-oscillations caused by the torsional mode of oscillations of the cutter. The frequency
of self-oscillations was 2.6 kHz, but due to the presence of impacts of the cutting edge, the
amplitudes of multiple harmonics with frequencies up to 10 kHz appeared in the spectrum.
On the the surface shows traces of impacts with a frequency of 20 microns. Such defects are
not visually noticeable, but they reduce the cleanliness and service life of the part. Such self-
oscillations often occur when working with a tool with a long overhang, but there are situations
when a decrease in dynamic stiffness in the low-frequency region causes high-frequency self-
oscillations of the cutting tool [12].
36 Stanochniy park