Page 224 - Fundamentals of Management Myths Debunked (2017)_Flat
P. 224
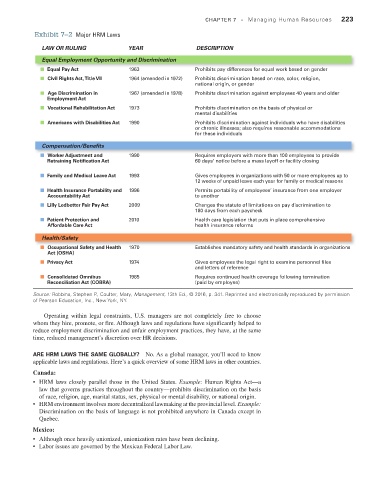
Exhibit 7–2 Major HRM Laws CHAPTER 7 • Managing Human Resources 223
LAW OR RULING YEAR DESCRIPTION
Equal Employment Opportunity and Discrimination
Equal Pay Act 1963 Prohibits pay differences for equal work based on gender
Civil Rights Act, Title VII 1964 (amended in 1972) Prohibits discrimination based on race, color, religion,
national origin, or gender
Age Discrimination in 1967 (amended in 1978) Prohibits discrimination against employees 40 years and older
Employment Act
Vocational Rehabilitation Act 1973 Prohibits discrimination on the basis of physical or
mental disabilities
Americans with Disabilities Act 1990 Prohibits discrimination against individuals who have disabilities
or chronic illnesses; also requires reasonable accommodations
for these individuals
Compensation/Benefits
Worker Adjustment and 1990 Requires employers with more than 100 employees to provide
Retraining Notification Act 60 days’ notice before a mass layoff or facility closing
Family and Medical Leave Act 1993 Gives employees in organizations with 50 or more employees up to
12 weeks of unpaid leave each year for family or medical reasons
Health Insurance Portability and 1996 Permits portability of employees’ insurance from one employer
Accountability Act to another
Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act 2009 Changes the statute of limitations on pay discrimination to
180 days from each paycheck
Patient Protection and 2010 Health care legislation that puts in place comprehensive
Affordable Care Act health insurance reforms
Health/Safety
Occupational Safety and Health 1970 Establishes mandatory safety and health standards in organizations
Act (OSHA)
Privacy Act 1974 Gives employees the legal right to examine personnel les
and letters of reference
Consolidated Omnibus 1985 Requires continued health coverage following termination
Reconciliation Act (COBRA) (paid by employee)
Source: Robbins, Stephen P., Coulter, Mary, Management, 13th Ed., © 2016, p. 341. Reprinted and electronically reproduced by permission
of Pearson Education, Inc., New York, NY.
Operating within legal constraints, U.S. managers are not completely free to choose
whom they hire, promote, or fire. Although laws and regulations have significantly helped to
reduce employment discrimination and unfair employment practices, they have, at the same
time, reduced management’s discretion over HR decisions.
are hrm LaWS the Same gLobaLLy? No. As a global manager, you’ll need to know
applicable laws and regulations. Here’s a quick overview of some HRM laws in other countries.
Canada:
• HRM laws closely parallel those in the United States. Example: Human Rights Act—a
law that governs practices throughout the country—prohibits discrimination on the basis
of race, religion, age, marital status, sex, physical or mental disability, or national origin.
• HRM environment involves more decentralized lawmaking at the provincial level. Example:
Discrimination on the basis of language is not prohibited anywhere in Canada except in
Quebec.
Mexico:
• Although once heavily unionized, unionization rates have been declining.
• Labor issues are governed by the Mexican Federal Labor Law.