Page 371 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 371
Intervertebral disk disease and other degenerative disorders 361
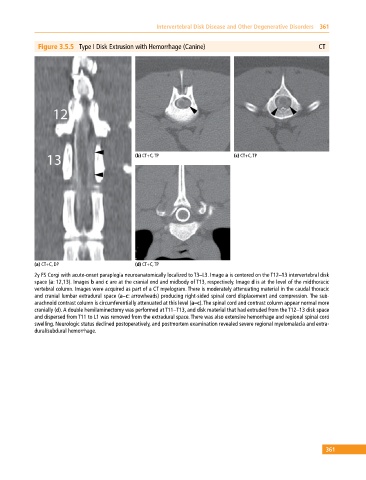
Figure 3.5.5 Type I Disk Extrusion with Hemorrhage (Canine) CT
(b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
(a) CT+C, DP (d) CT+C, TP
2y FS Corgi with acute‐onset paraplegia neuroanatomically localized to T3–L3. Image a is centered on the T12–13 intervertebral disk
space (a: 12,13). Images b and c are at the cranial end and midbody of T13, respectively. Image d is at the level of the midthoracic
vertebral column. Images were acquired as part of a CT myelogram. There is moderately attenuating material in the caudal thoracic
and cranial lumbar extradural space (a–c: arrowheads) producing right‐sided spinal cord displacement and compression. The sub
arachnoid contrast column is circumferentially attenuated at this level (a–c). The spinal cord and contrast column appear normal more
cranially (d). A double hemilaminectomy was performed at T11–T13, and disk material that had extruded from the T12–13 disk space
and dispersed from T11 to L1 was removed from the extradural space. There was also extensive hemorrhage and regional spinal cord
swelling. Neurologic status declined postoperatively, and postmortem examination revealed severe regional myelomalacia and extra
dural/subdural hemorrhage.
361