Page 546 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 546
536 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
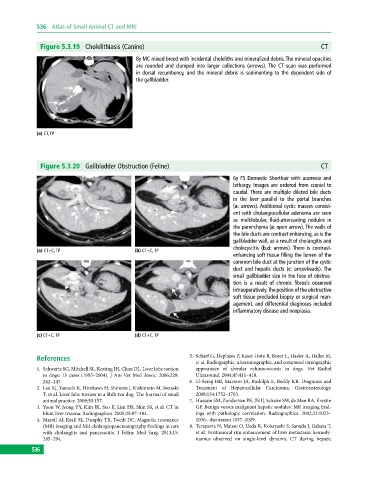
Figure 5.3.19 Cholelithiasis (Canine) CT
8y MC mixed breed with incidental choleliths and mineralized debris. The mineral opacities
are rounded and clumped into larger collections (arrows). The CT scan was performed
in dorsal recumbency, and the mineral debris is sedimenting to the dependent side of
the gallbladder.
(a) CT, TP
Figure 5.3.20 Gallbladder Obstruction (Feline) CT
6y FS Domestic Shorthair with anorexia and
lethargy. Images are ordered from cranial to
caudal. There are multiple dilated bile ducts
in the liver parallel to the portal branches
(a: arrows). Additional cystic masses consist-
ent with cholangiocellular adenoma are seen
as multilobular, fluid‐attenuating nodules in
the parenchyma (a: open arrow). The walls of
the bile ducts are contrast enhancing, as is the
gallbladder wall, as a result of cholangitis and
cholecystitis (b,d: arrows). There is contrast‐
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, TP
enhancing soft tissue filling the lumen of the
common bile duct at the junction of the cystic
duct and hepatic ducts (c: arrowheads). The
small gallbladder size in the face of obstruc-
tion is a result of chronic fibrosis observed
intraoperatively. The position of the obstructive
soft tissue precluded biopsy or surgical man-
agement, and differential diagnoses included
inflammatory disease and neoplasia.
(c) CT+C, TP (d) CT+C, TP
References 5. Scharf G, Deplazes P, KaserHotz B, Borer L, Hasler A, Haller M,
et al. Radiographic, ultrasonographic, and computed tomographic
1. Schwartz SG, Mitchell SL, Keating JH, Chan DL. Liver lobe torsion appearance of alveolar echinococcosis in dogs. Vet Radiol
in dogs: 13 cases (1995–2004). J Am Vet Med Assoc. 2006;228: Ultrasound. 2004;45:411–418.
242–247. 6. ElSerag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L, Reddy KR. Diagnosis and
2. Lee KJ, Yamada K, Hirokawa H, Shimizu J, Kishimoto M, Iwasaki Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Gastroenterology.
T, et al. Liver lobe torsion in a Shihtzu dog. The Journal of small 2008;134:1752–1763.
animal practice. 2009;50:157. 7. Hussain SM, Zondervan PE, JN IJ, Schalm SW, de Man RA, Krestin
3. Yoon W, Jeong YY, Kim JK, Seo JJ, Lim HS, Shin SS, et al. CT in GP. Benign versus malignant hepatic nodules: MR imaging find
blunt liver trauma. Radiographics. 2005;25:87–104. ings with pathologic correlation. Radiographics. 2002;22:1023–
4. Marolf AJ, Kraft SL, Dunphy TR, Twedt DC. Magnetic resonance 1036– discussion 1037–1029.
(MR) imaging and MR cholangiopancreatography findings in cats 8. Terayama N, Matsui O, Ueda K, Kobayashi S, Sanada J, Gabata T,
with cholangitis and pancreatitis. J Feline Med Surg. 2013;15: et al. Peritumoral rim enhancement of liver metastasis: hemody
285–294. namics observed on singlelevel dynamic CT during hepatic
536