Page 578 - Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
P. 578
568 Atlas of Small Animal CT and MRI
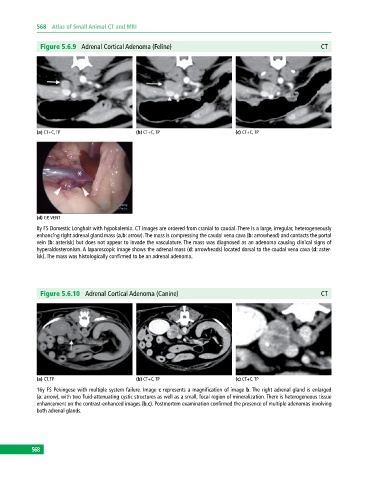
Figure 5.6.9 Adrenal Cortical Adenoma (Feline) CT
(a) CT+C, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
(d) GP, VENT
8y FS Domestic Longhair with hypokalemia. CT images are ordered from cranial to caudal. There is a large, irregular, heterogeneously
enhancing right adrenal gland mass (a,b: arrow). The mass is compressing the caudal vena cava (b: arrowhead) and contacts the portal
vein (b: asterisk) but does not appear to invade the vasculature. The mass was diagnosed as an adenoma causing clinical signs of
hyperaldosteronism. A laparoscopic image shows the adrenal mass (d: arrowheads) located dorsal to the caudal vena cava (d: aster-
isk). The mass was histologically confirmed to be an adrenal adenoma.
Figure 5.6.10 Adrenal Cortical Adenoma (Canine) CT
(a) CT, TP (b) CT+C, TP (c) CT+C, TP
16y FS Pekingese with multiple system failure. Image c represents a magnification of image b. The right adrenal gland is enlarged
(a: arrow), with two fluid‐attenuating cystic structures as well as a small, focal region of mineralization. There is heterogeneous tissue
enhancement on the contrast‐enhanced images (b,c). Postmortem examination confirmed the presence of multiple adenomas involving
both adrenal glands.
568